I’m sure many of you have heard about the opioid crisis from your friends or on the news, but some of you, like me, may not know exactly how it started and why it became an epidemic.
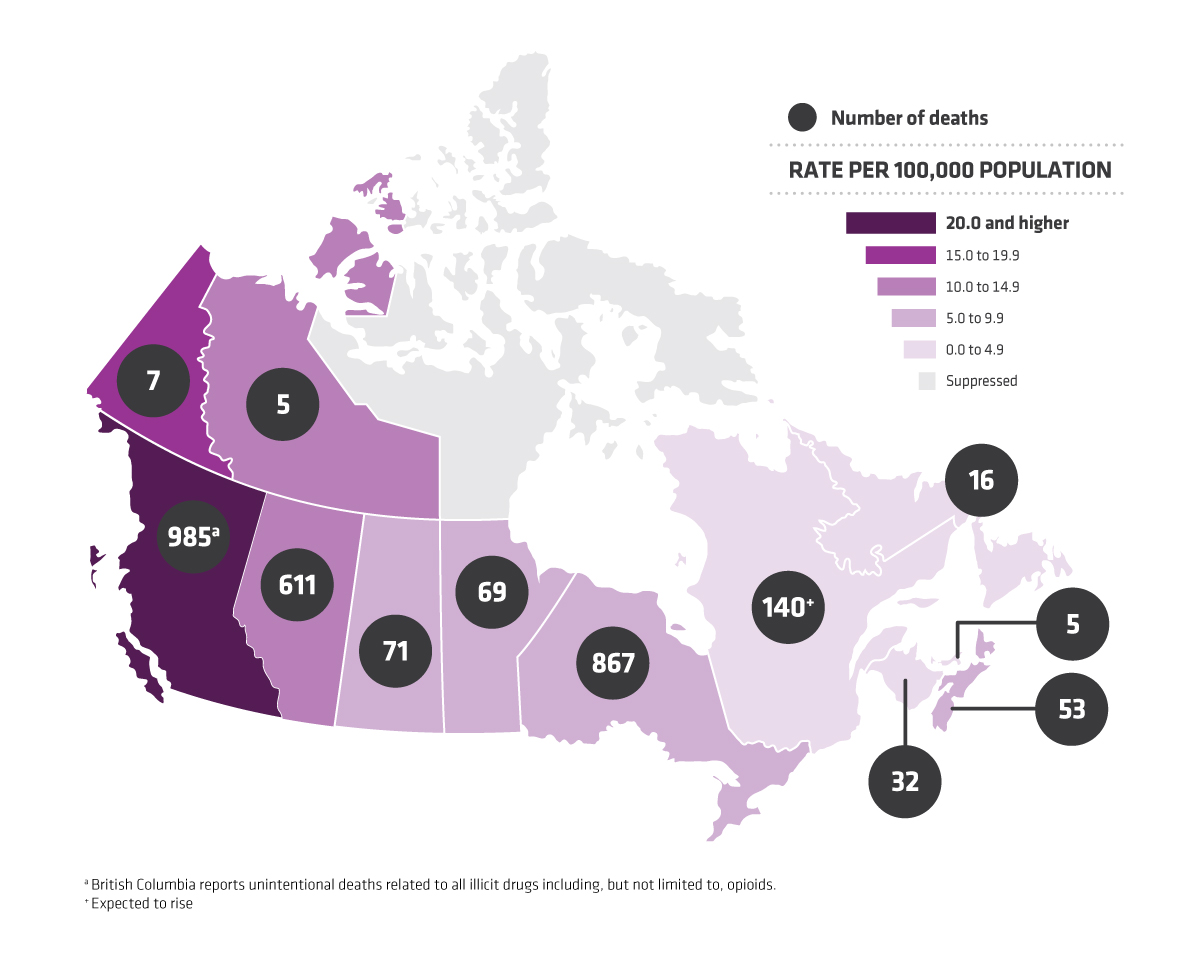
In 2016, there were about 42,249 opioid overdoses in the United States and about 2,800 opioid-related deaths in Canada. British Columbia is the epicenter of the crisis in Canada with more than 1,400 deaths from drug overdoses last year, and about 81% involved fentanyl.
Opioids are natural and synthetic chemicals that act on opioid receptors in your brain and body, and it is often prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain. Opioid receptors are located in reward centers of the brain and in areas that control pain. When opioids bind to these receptors, it inhibits pain and it can create intense feelings of euphoria. This is what makes them so addictive. Furthermore, our body builds tolerance to it pretty quickly, so it takes more of the drug to deal with the same amount of pain. This can be physically and psychologically demanding and can lead to feelings of withdrawal.
In the 1990s, doctors started prescribing more painkillers to try to treat pain. With the opioid epidemic, it was thought that many people who took the drug that was prescribe, started to take more of it. When pills became expensive and hard to get, they looked for other alternatives such as heroin which is more readily available. The addiction can become deadly because opioid receptors are not only located in areas that control pain and emotion, but in areas that control breathing as well. When they block signalling there, it can slow down and even stop breathing.
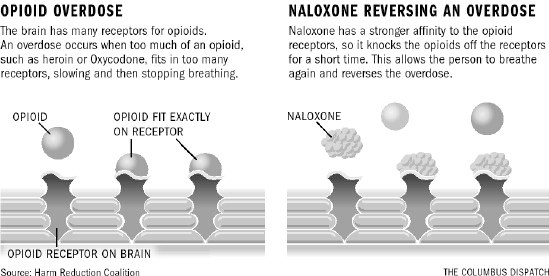
However, we do have some ways to counteract opioids such as the use of naloxone. Naloxone can bind to opioid receptors without causing any unusual effects. It works quite well because it binds to opioid receptors more strongly than the overdosed drug, so it can flood your system and prevent it from binding. However, it has to be given immediately because it doesn’t take long after an overdose to cause you to stop breathing. It’s especially true if you take fentanyl, a stronger synthetic opioid.
Fentanyl is 50 to 100 times stronger than morphine and it can be added into heroin and other opioids. Furthermore, fentanyl can be absorbed through the skin and breathing it can kill you.
Source: CBC News
Although I don’t use opioids, I do take tylenol when I am sick, which is a non-opioid pain medication that produce moderate feelings of euphoria. And trust me, it is a very good feeling when you are feeling ill. Therefore, I can see why opioids can be very addicting to those who are in substantial pain.
However, currently, doctors are trying to prescribe fewer opioids, and researchers are trying to find and develop opioids that can kill pain without all the negative effects associated to it.
Source: MSNBC
– Tammy Tang


/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/58540999/908889612.jpg.0.jpg)