Ghosts and paranormal activity – how can they be explained? For hundreds of years, people have reported ghost sightings and have experienced spine-chilling noises.
Science, on the other hand, yet again seems to debunk these claims.
Infrasound
Infrasound refers to low frequency sound, between 0.1 and 20 Hz, just below the range of human hearing.
A study done by Vic Tandy in 1998 called “The Ghost in the Machine” became popular due to its relatability to ostensible haunting. Tandy decided to pursue this experiment due to his lab evoking an anxiety-inducing environment. One day, Tandy was hearing vibrational noises from a nearby fan. As one would, Tandy measured the vibrational frequency of this fan, and found that it was emitting a frequency of 19 Hz, a frequency below the threshold of human hearing. When the fan was turned off, the anxiety-inducing feeling in the room disappeared because the emitted energy from the 19Hz stopped., which was likely causing the eerie feelings.
Most of the time, when we sense a paranormal phenomenon, it is the recognition center of the temporal lobe that interprets changing sounds and processes them back to us through eerie and unsteady feelings.
Electromagnetic Radiation
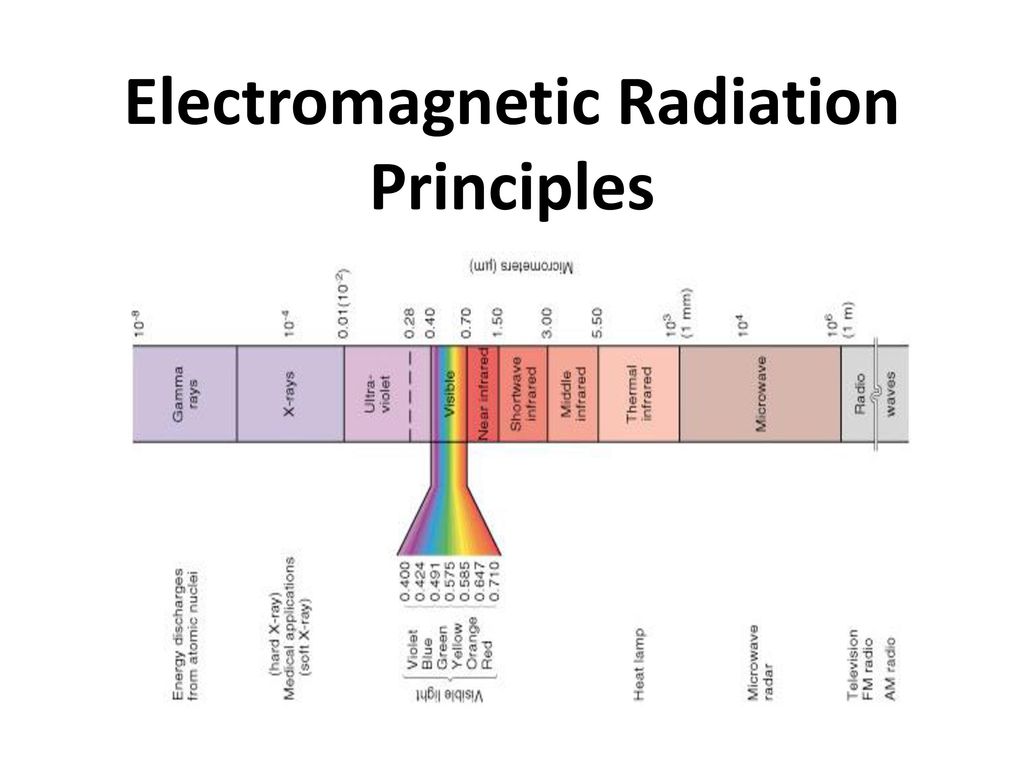
Image represents the electromagnetic spectrum, and the wavelength associated with each type of radiation. From Electromagnetic Radiation Principles, Published by Chastity Bailey, showing the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is used to describe the waves present in the electromagnetic field that carry electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic energy is changing around us, through our electronic devices, power lines and signals emitted through the aforementioned. Changing electromagnetic energy creates disturbances that behave like waves and has an effect on human behaviour and perception.
To learn more specifics about electromagnetic radiation, listen to this podcast:
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
Source: Astronomy Cast
Could Our Brains be Playing Tricks on Us?
A study done by Joseph M. Barnby and Vaughan Bell attempted to validate the sense of a paranormal presence through psychological factors. The ‘sensed presence’ refers to our subjective experiences of an external entity around us. It was found that the feeling of ‘sensed presence’ was due to feelings of fear and anxiety, and so the unsettling feeling of experiencing an abnormal entity was a stress response generated by the brain.
Barnby and Bell concluded that the feelings felt from ‘sensed presences’ were primarily due to religious beliefs and psychiatric and neurological conditions.
This Ted Talk presents another view on our perceptions:
Video discusses the ways in which people perceive experiences and explains potential differing factors.
Source: Ted.com
We all have differing opinions about this topic, and whether you believe the science or spiritual side of the discussion, one aspect still remains the same for everyone: experiencing paranormal activity can definitely be terrifying.
by: Sofia Savkovic
















 picture courtesy: Daniel Koditschek
picture courtesy: Daniel Koditschek