Throughout the Sep-Dec, 2010 term, I worked with an astronomy instructor to create a more learner-centered classroom. As I described elsewhere, we spent just over one third of the instructional time on interactive activities: think-pair-share using clickers, lecture-tutorial worksheets, ranking tasks and a couple of predict-observe demonstrations. And it resulted in a learning gain of 0.42 on a particular assessment tool, the LSCI. That means the students learned 42% of the concepts they didn’t already know at the beginning of the term. That’s not bad — we’re pretty happy with it.
So, students can learn in a learner-centered classroom. But maybe they can learn in a more traditional classroom, too.
We don’t have LSCI data from previous years (note to self: think ahead! Collect standardized assessment data on classes before attempting any transformations!) To investigate if transforming the instruction class makes any difference, we re-used, word-for-word, a handful of questions from the same instructor’s 2008 Final Exam (pre-transformation) on this term’s Final Exam: 10 multiple-choice questions and 4 longer-answer questions. We made sure the questions assessed the concepts we covered in 2010 in sync with the learning goals.
I extracted students’ marks on these 14 questions from the 2010 exams (N=144). And from the old, 2008 exams (N=107), being sure to re-mark the longer-answer questions using the 2010 rubric. (Note to self #2: buy aspirin on the way home.)
What were we hoping for? Significant increase in student success in the transformed, learner-centered course.
How I wish I could report that’s what we found. But I can’t. Because we didn’t. Here are the results:
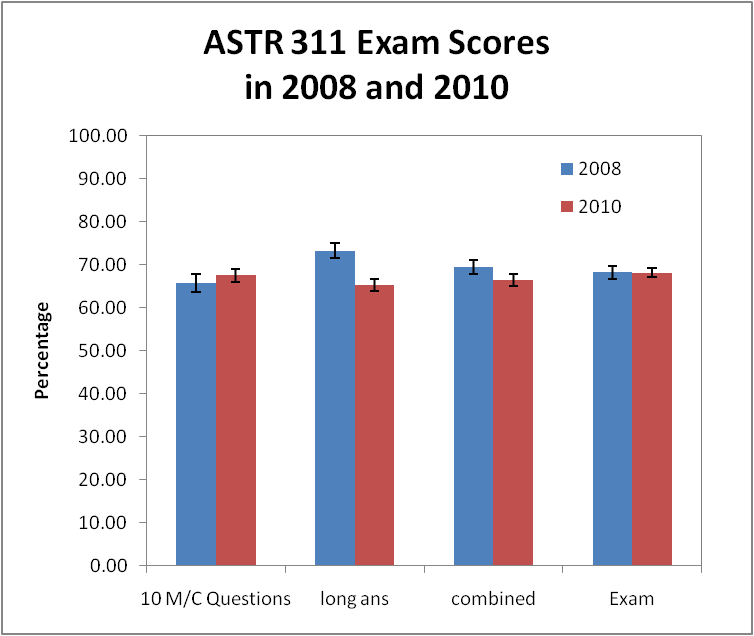
Students scores on questions used on both the 2008 and 2010 Final Exams in the introductory astronomy course, ASTR 311. Error bars are standard error of the mean.
There is no significant difference in student success on the 10 multiple-choice questions. Their scores on the entire exams are also the same, though the exams are not identical, only about 1/4 of the 2008 exam is re-used in 2010. Nevertheless, these nearly identical Exam scores suggest the populations of students in 2008 and 2010 are about the same. There are are differences in the 4 long-answer questions: the 2008 students did better than their 2010 counterparts.
Two things jumped out at me
- Why did they do so much better on the long-answer questions? I said we used the same marking rubric but we didn’t use the same markers. A team of teaching assistants marked the 2010 exams; I(re) marked the 2008 exams. The long-answer questions are work 10 marks, so a little more (or less) generosity in marking – half a mark here, half a mark there – could make a difference. I really need to get the same TAs to remark the 2008 exams. Yeah, like that’s gonna happen voluntarily. Hmm, unless there’s potential for a publication in the AER…
- Why, oh why, didn’t they do better this year? Even if we omit the suspicious long-answer marks and look only at the multiple-choice questions, there is no difference. Did we fail?
No, it’s not a failure. The instructor reduced her lecturing time by 35%. We asked the students to spend 35% of their time teaching themselves. And it did no harm. The instructor enjoyed this class much than in 2008. We had consistent 75% attendance (it was much lower by the end of the term in 2008) and students were engaged in material each and every class. I think that’s a success.
The next step in this experiment is to look for retention. There is evidence in physics (see Pollock & Chasteen, “Longer term impacts…” here) that students who engage in material and generate their own knowledge retain the material longer. With that in mind, I hope to re-test these 2010 students with LSCI in about 3 months, after they’ve had a term to forget everything. Or maybe not…