Henry Giroux, Thruthout, January 13, 2014– The Gilded Age is back, with huge profits for the ultrarich, hedge fund managers and the major players in the financial service industries. In the new landscapes of wealth, exclusion and fraud, the commanding institutions of a savage and fanatical capitalism promote a winner-take-all ethos and aggressively undermine the welfare state and wage a counter revolution against the principles of social citizenship and democracy. The geographies of moral and political decadence have become the organizing standard of the dreamworlds of consumption, privatization, surveillance and deregulation. For instance, banks such as JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America and other investment companies including Barclays, Citigroup, Deutsche Bank, Goldman Sachs, and UBS prosper from subterfuge and corruption. They also have been transformed into punishing factories that erode the welfare state while pushing millions into hardship and misery and relegating an entire generation of young people into a state of massive unemployment, debt, and repression. The profits seem endless and the lack of moral responsibility unchecked as the rich go on buying sprees soaking up luxury goods in record numbers. The New York Times reports that dealers of high-end luxury cars cannot keep up with the demand. Indulging in luxury items is no longer a dirty word for the ultrarich in spite of living in a society wracked by massive unemployment, inequality and poverty. One example provided by the Times, without either irony or criticism, points to “Matt Hlavin, an entrepreneur in Cleveland who owns seven businesses, mostly in manufacturing, bought three Mercedes last year: a $237,000 SLS AMG and a $165,000 S63 AMG for himself, and a $97,000 GL550 sport utility vehicle for his wife.”[1] This example of shameless consumption reads like a scene out of Martin Scorsese’s film The Wolf of Wall Street, which portrays the financial elite as infantilized frat boys out of control in their unquenchable craving for greed, sex, power, and every other debauchery imaginable.[2] At a time when the United States has descended into forms of political and moral amnesia, massive inequity and high levels of poverty, coupled with narratives of excess and over-the-top material indulgence, have become normalized and barely receive any critical commentary in the mainstream media.
It gets worse. As the zombies of casino capitalism rake in unprecedented amounts of wealth, they appear to take delight in mocking and humiliating the poor and disadvantaged as if they are not only responsible for their suffering but deserve such hardships in spite of the fact they are not accountable for the difficulties in which they find themselves. Those with little power or wealth are now seen not only as morally degenerates but as disposable, subject to the whims of the market and outside any consideration of compassion or justice. Yet there is more at work here than a moral deficit or the kind of pathological daring and willingness to remove oneself from any sense of compassion for others. There is also a culture of cruelty willfully reproduced by a rabid form of casino capitalism that measures human worth in cost-benefit analysis and accrues and consolidates power in the interests of the top one percent of the population.
The new extremists balk at extending unemployment benefits or providing food stamps for young children. Yet, they have no trouble offering millions in subsidies to corporate interests or lowering taxes for the ultrarich corporations. Obscene wealth couples with the arrogance of power as billionaires such as the Koch brothers make 3 million dollars an hour from their investments while simultaneously calling for the abolishment of the minimum wage.[3] CEO salaries reach into the financial stratosphere, while the middle and working classes increasingly face impoverishment and misery. In 2012, the “top 10 percent took in half of the country’s total income” while the top 1 percent took more than one-fifth (22.5 percent) of the income earned by Americans. [4] In the midst of the upward redistribution of wealth, misery proliferates, and the commanding institutions of society are increasingly more divorced from maters of ethics, social responsibility and social costs. This is evident as the ranks of homeless children grow exponentially, while corporate fat cats fund various groups to lobby against health care policies and social provisions for the poor. It is also evident in the growing ranks of people on food stamps, an increase in the homeless population, especially among children. Moreover, 46.2 percent of the American population lives in poverty. [5]
Republicans claim they are now concerned about addressing poverty, especially since the general public rightly views them as heartless, cruel and indifferent to the hardships experienced by people who are unemployed and lack food, shelter, health care and any sense of hope. Yet, the hypocrisy of the apostles of casino capitalism is on full display in a commentary by The New York Times which states: “But at the same time that the party is shifting its focus to poverty, many Republicans are pushing for deep cuts to food assistance programs and unemployment insurance, while 11 million Americans are jobless and poverty rates remain elevated in the wake of the recession.” [6] For the right-wing extremists dominating government, the courts and cultural life, talk about choice and agency is divorced from social responsibility and the emphasis on individual responsibility is nothing more than a cheap trick to divert the public’s attention away from larger structural and systemic problems facing the United States.
We now live under a form of casino capitalism that revels in deception, kills the radical imagination, depoliticizes the American public and promulgates what might be called disimagination factories and punishing machines. Idealism has been replaced by a repressive punishing machine and a surveillance state that turns every space into a war zone, criminalizes social problems and legitimates state violence as the most important practice for addressing important social issues. Racism now fuels a mass incarceration system that expands the reach of the punishing state to those viewed as excess and excluded from American society. The carceral state and the surveillance state now work together to trump security over freedom and justice while solidifying the rule of the financial elite and the reigning financial services such as banks, investment houses and hedge funds, all of which profit from the expanding reach of the punishing state. The drug war has become a war on racial minorities just as the war on poverty has become a war on the poor.
Chris Hedges is right when he argues that “any state that has the capacity to monitor all its citizenry, any state that has the ability to snuff out factual public debate through [the] control of information, any state that has the tools to instantly shut down all dissent is totalitarian.” [7] While Hedges is aware that this disciplinary culture of fear and repression is rooted in a political economy that treats people as objects and makes the accumulation of capital the subjects of history, he underestimates one important element of the new authoritarianism produced by casino capitalism. That is, what is novel about existing registers of discipline and control is that they operate in a new historical conjuncture in which the relationship among political power, cultural institutions and everyday life has become more powerful and intense in the ability to undermine the radical imagination and the power and capacities of individuals to resist repression and make the crucial decisions necessary to take control over the forces that shape their lives. The machineries of public pedagogy and consent have taken on an Orwellian presence in the age of digital technologies, and when challenges to authoritarian rule emerges, the state resorts to the overt and unapologetic repression of critical thought and dissent.
The anonymity of the corporate state becomes invisible as historical and public memory are erased and the American public is increasingly infantilized. Stupidity is normalized through a consumer/celebrity culture, and where that does not work, the machinery of state repression, with its endless culture of fear, punishes those willing to question authority. Authorities try to blind people to the courage exhibited by whistleblowers such as Chelsea Manning, Jeremy Hammond and Edward Snowden, painting them instead as traitors. Courage is now under attack by the sterile and dangerous call for unchecked security. Fear becomes the only value left in the arsenal of the machinery of surveillance, control and social death. David Graeber is right in arguing that the call for public dialogue, dissent and critical exchange in order to hold power accountable no longer provokes informed judgement and outrage among the public or thoughtful responses from politicians and popular pundits. On the contrary, he writes:
Objections to such arrangements are to be met with truncheons, lasers, and police dogs. It’s no coincidence that marketization has been accompanied by a new ethos where challenge is met with an instant appeal to violence. In the end, despite endless protests to the contrary, our rulers understand that the market is not a natural social arrangement. It has always had to be imposed at the point of a gun . . . The question to ask now is not, how do we bring it back. That’s impossible and quite undesirable. The question is what new forms of genuinely democratic self-organization might rise from its ashes? To even begin to ask this question we must first of all get rid of the police. [8]
American politics and culture have been handed over to the rich, lobbyists for the corporate elite, and now function largely to produce a state that offers the ultrawealthy and powerful all of the benefits they need to accumulate even more capital, regardless of the massive inequality in wealth, income and suffering such policies produce. In spite of being discredited by the economic recession of 2008, unfettered casino capitalism remains a dominant force and continues to produce runaway environmental devastation, egregious amounts of human suffering and the reinforcement of what Charles Ferguson has called “finance as a criminalized, rogue industry. [9] And, yet, while resistance to such measures is growing, it is far too weak to offer a significant challenge to the new authoritarianism.
All over the world, the forces of casino capitalism are invoking austerity measures that produce a kind of social and civil death as they dismantle the historically guaranteed social provisions provided by the welfare state, defining profit-making as the essence of democracy, expanding the role of corporate money in politics, waging an assault on unions, augmenting the military-security state, overseeing widening social inequality, promoting the erosion of civil liberties, and undercutting public faith in the defining institutions of democracy. The script is not new, but the intensity of the assault on democratic values, civic engagement and public service has taken a dangerous turn and provides the ideological, political and cultural foundation for a society that seems unaware it is in the midst of an authoritarian stranglehold on all of its most cherished institutions, ranging from schools and health care to the very foundation of democracy. Austerity has become the weapon of choice, an economic poison designed to punish the middle and working classes while making clear that casino capitalism will administer the most severe penalties to those who challenge its authority. The police have become the new private armies of the rich, designed to keep the public in check hoping to make them fearful of being exposed to police brutality, state violence or the expanding mechanisms of the multiple surveillance apparatuses that now collect every piece of information that circulates electronically. Conformity has become the order of the day and fear the new norm, reinforced by a disimagination machine and the punishing state now mutually informing each other.
Within the last 30 years, the United States has been transformed from a society that included a market economy subject to the rule of the state to a society and government that are now dominated almost exclusively by market values and corporate power. We now live in what Robert Jay Lifton once described as a “death-saturated age.” [10] Political authority and power have been transformed into a sovereignty of corporate governance and rule. The United States has moved from a market economy to a market society in which all vestiges of the social contract are under attack, and politics is ruled by the irrational notion that casino capitalism should govern not simply the economy but the entirety of social life. With the return of the new Gilded Age, not only are democratic values and social protections at risk, but the civic and formative cultures that make such values and protections central to democratic life are in danger of disappearing altogether.
Public and higher education, however deficient, were once viewed as the bedrock for educating young people to be critical and engaged citizens. Schooling was valued as a public good, not a private right. Many educators in the ’70s and ’80s took seriously Paulo Freire’s notion of problematizing education, in which he called for students to be taught modes of critical literacy in which they could not only read the word but also read the world critically. [11] According to Freire, young people should be taught to read and write from a position of agency. This meant learning how to engage in a culture of questioning, restaging power in productive ways, and connecting knowledge to the exercise of self-determination and self-development. Freire’s notion of critical pedagogy and education for freedom denounced banking education because it viewed students as passive containers into which knowledge was endlessly deposited. Rather than allow students to develop their own meanings, banking education assigned meanings for them, largely to memorize and spit out on intellectually bankrupt forms of testing. [12] Banking education is back with a vengeance and ironically parades under the name of educational reform, common standards and race to the top. Public education has become a site of pedagogical repression, robbing students of the ability to think critically as a result of the two political business parties’ emphasis on education as mainly a project of mindless testing, standardization and the de-skilling of teachers. In addition, school reform has become a euphemism for turning public schools over to private investors who are more concerned about making money than they are about educating young people. On the other hand, low-income and poor minority students increasingly find themselves in schools in which the line between prison culture and school culture is blurred.
Higher education, especially in the post-World War II period through the ’60s and ’70s, was, however ideally, considered a place where young people were taught how to think, engage in critical dialogue, and take on the responsibilities of informed and critical citizens. Now such students are subject to a technically trained docility, defined largely as consumers and told that the only value education has is to prepare them to be workers and consumers ready and eager to serve the ideological and financial interests of the global economy. Critical thought and the radical imagination have become a liability under casino capitalism and for a growing number of institutions the enemy of public and higher education because they hold the potential to be at odds with the reproduction of a criminogenc culture in which greed, unchecked power, political illiteracy and unbridled self-interest work to benefit the wealthy and corporate elite. Under such circumstances, education becomes simply a business, developing an obsession with accountability schemes, measurable utility, authoritarian governing structures, and a crude empiricism for defining what counts as research.
How else to explain the following comment made by the president of Macomb Community College in Michigan: “Macomb is working with the federal government and other community colleges to better prepare students for the world that exists, not the world they want to live in.” [13] Or for that matter the blatant anti-intellectual bias imposed on colleges in Florida where Governor Rick Scott wants to push students toward business-friendly degrees by lowering tuition for academic fields and subjects that “steer students toward majors that are in demand in the job market.” [14] Of course, those areas such as philosophy, sociology, music, the arts, and other mainstays of the liberal arts would be more costly and their demise would intensify. Graeber argues that this assault on higher education has now become an object of intense state violence. He writes:
Make no mistake: to threaten someone with a stick is the ultimate anti-intellectual gesture. And if one thing has become clear in recent months, this is the first – really the only – impulse of the current government when faced with challenges to their vision for higher education. Police infiltration, surveillance, elected student leaders banned from political activities on campus, the arrest of students for simple acts of expression like chalking slogans on sidewalks, send a clear and constant message. There can be no reasoned discussion on these issues. There is no longer anything to talk about. Certainly, democracy has absolutely nothing to do with it. The pursuit of knowledge and understanding have been declared nothing but a consumer product, or else a form of technical training to increase overall economic productivity; these are the only way these matters can be discussed; if anyone wishes to gather to object to this, to gather in places of learning to insist that knowledge and understanding are not mere economic goods but something precious and valuable in their own right, they can only do so by permission of those who are telling them otherwise; otherwise, they can expect to be physically attacked. [15]
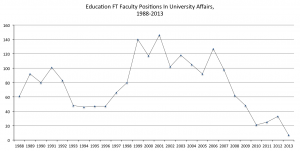
Similarly, higher education has become a dead zone for killing the imagination, a place where ideas that don’t have practical results go to die and where faculty and students are punished through the threat of force or harsh disciplinary measures for speaking out, engaging in dissent and holding power accountable. Faculty in most universities have been reduced to part-time jobs and function as indentured servants with no benefits, shockingly low salaries and no power to shape the conditions under which they work. With over 70 percent of faculty now holding the status of contingent labor, they are increasingly becoming one of the largest groups of professionals that qualify for food stamps to survive. These contingent and debt-ridden faculty live in a culture in which time is a burden rather than a luxury and have few opportunities to research, write and engage important social issues. At the same time, they live under both a survivalist mode and a culture of fear knowing that they can be dismissed arbitrarily at any time for the slightest infraction. Even tenured faculty are feeling the heat of a business-oriented de-democratizing university. For example, the Kansas Board of regents recently drastically curtailed tenure and academic freedom by claiming that both tenured and non-tenured faculty who used social media in ways that were not in the interest of the university, decided exclusively by the CEO of the university, were subject to dismissal. Speech that now impairs or reduces the university’s “efficiency” overrides the right of faculty to exercise free speech or address issues they deem socially and politically important. For all intent and purposes, this signifies not only the end of tenure but academic freedom. Moreover, as William Black points out, “in both substance and dishonesty of presentation, the Regents’ policy is literally Orwellian.” [16]
Read More: Truthout


 Follow
Follow






UBC Sauder Business admin, still no accountability? #ubc #ubcsauderschool #mba #bcpoli #bced #yteubc
Call this and this research, call it evaluative opinion, call the facts, facts. Perhaps cheer-fully, perhaps not, UBC campus waits for accountability over the Sauder rape cheer.
Thus far, President Toope’s Measures fail to effect any form of accountability at the top. For example, the last measure, “[Dean] Helsley announced that the Sauder School of Business will no longer support the CUS FROSH events,” is meaningless, if according to a.nony.mouse in the Ubyssey comments section, “the CUS is its own entity and operates separately from the administration, something that has also been made clear in all investigative documents to date.”
I guess it is plausible that former Dean Muzyka micro-managed the students for over a decade and once he left, the repressed returned and they went wild, so to speak. But I don’t buy this narrative.
Instead, I stand with Nathan in the Ubyssey comments, “there is some fault on the part of the administration.” There may be, as Harbinder says, a “culture of shallowness” and as I say a “culture of entitlement.” For the record, I’ve worked with excellent students and faculty from Sauder, but evidently something (or someone) is failing at the top.
The facts speak: In the fact-finding report, curiously, the words “administration” and “administrator” do not appear while “student/s” appears 46 times. There were no facts to find on administrators or administration?
If it is plausible that of the 11 Assistant and Associate Deans + Dean Helsley, none have responsibilities for “students” in their portfolio, then the President’s Office has failed. That’s a fact of administrative bloat: Between 1999 and 2013, this Faculty’s administrators at that level more than doubled. Yes, Sauder has Dean Muzyka to thank. And increasing tuition and fees have that to factor in. Yet none of these 12 now have any responsibilities for students? I don’t buy that. So is the buck or loonie passed back to the Sauder Dean’s Office?
Similarly, someone or something is failing at the top if of the 12 senior administrators none have curriculum in their portfolio. I find it incomprehensible that it has taken this cheer, a fact-finding report, campus outrage, and nearly 2014 for Sauder to finally get around to, announced on 1 November by Dean Helsley, “Implementing changes in the curriculum to enhance themes of social justice, ethics, gender and cultural sensitivity, and their role in corporate social responsibility and the creation of a civil society”?
A top business school finally getting around to this? In this economy and world? There are 12 senior administrators and none have curriculum and courses in their portfolio? What exactly are they doing? Not all can be running around consulting, like Bob Sutton, teaching CEOs how not to be assholes.
Comments Off on UBC Sauder Business admin, still no accountability? #ubc #ubcsauderschool #mba #bcpoli #bced #yteubc
Posted in Academic freedom, Accountability, Administration, Campus Life, Commentary, Environment, Equity, Ethics, Governance, Research, Students, Working conditions
Tagged Administration, Faculty, Organizing, Students, Working conditions