Habitat
Takakia lepidozioides typically lives on rocks, often near waterfalls and in tundra. This is a photo of Dr. Schofield and Olivia looking for Takakia on rock surfaces beside a waterfall in Jervis Inlet.
Gametophyte
Overall Structure:
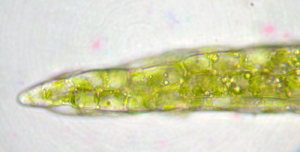
Takakia lepidozioides shoots are vivid green with radially and irregularly arranged leaves. Takakia lepidozioides has been mistaken as a leafy liverwort in the past, due to the leaf arrangement, and the presense of oil drops.
Leaf Structure:
Individual leaves are cylindrical, tapered, and divided or lobed two to four times.
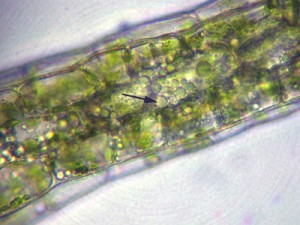
The leaves are typically tristratose and contain oil drops.
Axillary mucilage hairs are located at the leaf base.
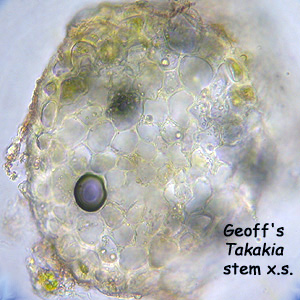
Stem:
The stem is composed of a cuticle and weak conducting strand, that are visible in cross-section.
Intercalary Rhizomatous Branches:
Shoots are connected by an intercalary rhizomatous branches. Shoots stand erect on the substratum from these branches. The intercalary rhizomatous branches do not have a cuticle and are colorless.
New stems and shoots arise from the intercalary rhizomatous branches.
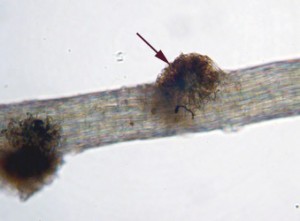
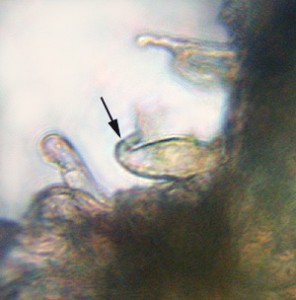
Some branches may contain clusters of beaked mucilage cells.
Beaked mucilage cells help maintain moisture, as Takakia lepidozioides does not tolerate dessication well.
Female Gametophyte:
The sexual structures are borne laterally. There is no difference between perigonial and perichaetial leaves.
Archegonia are flask-shaped and immersed among leaves.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction is cauducous. Leaves fall off readily, and serve as asexual propagules.
Sporophyte
No sporophytic material has been collected from Takakia lepidozioides.