Habitat
This epiphytic species is commonly found growing on the trunks of various trees; however it is frequently seen on broad-leaf maples. Even though M. menziesii mostly grows epiphytically, it is frequently found growing on rock surfaces that are dry and in the shade. The distribution of this species is wide, ranging from central Europe to western Asia and North Africa. Furthermore, it has a disjunct distribution occurring in western North America, from southeastern Alaska to California as well as in western Alberta, Montana and South Dakota [ref].
Gametophyte
Overall structure:
The gametophytes of this species can range in color, from rusty-brown to golden-brown to pale olive-green. These plants, which can be relatively large, form extensive mats on the trunk of trees. The apex of the leafy shoots often point downward. The shoots of the gametophyte are pinnately branched and occasionally produce many branchlets that are slender and fragile.
Leaves:
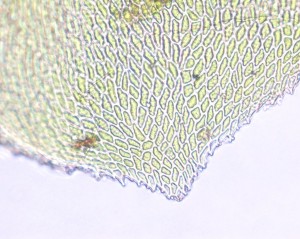
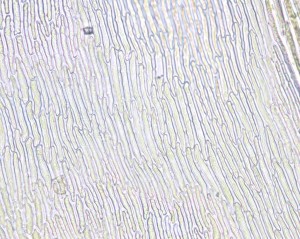
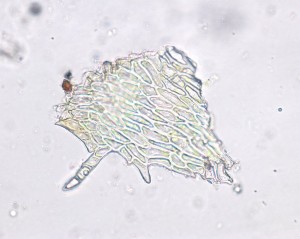
 The leaves are oblong and undulate. A costa is also present and extends to about ¾ of the length of the leaf.
The leaves are oblong and undulate. A costa is also present and extends to about ¾ of the length of the leaf.
The leaves are typically broad at the apex, ending abruptly in a pointed tip.
Leaf cells:
A closer look at the leaf cells will reveal that they are smooth, linear (proximally) to rhomboidal (distally) and often pitted.
Stem:
 The presence of small green paraphyllia can be observed on the stem. Paraphyllia are filamentous or leaf-like structures that grow along the stems of some mosses.
The presence of small green paraphyllia can be observed on the stem. Paraphyllia are filamentous or leaf-like structures that grow along the stems of some mosses.
The male gametophyte of M. menziesii often produces many small bulb-like perigonia on its lateral shoots.
Sporophyte
Overall structure:
 It has been noted that sporophytes are generally abundant in epiphytic populations, while they are less frequent on populations growing on rock surfaces.
It has been noted that sporophytes are generally abundant in epiphytic populations, while they are less frequent on populations growing on rock surfaces.
Sporangium:
 The sporangium is typically brown in color and more or less oblong in shape. It is immersed in a perichaetium on the underside of the main stems of female plants. The operculum, when present, is obliquely rostrate and the peristome is double.
The sporangium is typically brown in color and more or less oblong in shape. It is immersed in a perichaetium on the underside of the main stems of female plants. The operculum, when present, is obliquely rostrate and the peristome is double.
Seta:
 The seta is very short (<2 mm long) and hidden by the surrounding perichaetial leaves. Note how the perichaetial leaves differ in shape from the typical stem leaves.
The seta is very short (<2 mm long) and hidden by the surrounding perichaetial leaves. Note how the perichaetial leaves differ in shape from the typical stem leaves.
Spores:
The spores of this species are papillose.