Your body is constantly under attack from millions of pathogens every day and while most of the time the body’s immune system can take care of the invaders there are instances where outside help is needed. This is where antibiotics become useful. But currently problems are arising with the usage of antibiotics, mostly in the form that many current antibiotics are no longer effective against specific species of invading bacteria, these bacteria are termed antibiotic resistant bacteria. The problem of antibiotic resistant bacteria is one that if left unchecked will grow and might contribute to a mass outbreak of dangerous bacteria.
Antibiotics have become a prominent feature of modern health care and are used to fight and inhibit the growth of bacteria that have invaded your body. When the field of antibiotics was first discovered and expanded upon there was little to no general resistance to the antibiotics commonly used in today’s medical practices.
But resistance has grown as microbial mutations and the misuse of antibiotics has selected for dangerous antibiotic resistant bacteria. Bacteria replicate incredibly quickly and due to their methods of replication their genetic code, DNA, there will be a chance for mutations, random changes to the new DNA produced, in each new generation of bacteria. These mutations can often give bacteria a way of making certain antibiotics useless against them due to how they can change where the antibiotic interacts to interfere with the bacteria. While normally this chance of mutation is low for each bacteria, due to their fast replication rate mutations can appear quite frequently and cause problems for antibiotic treatments.
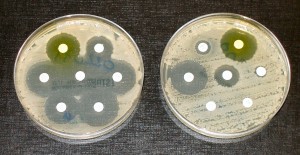
The bacteria grown in the petri dish on the left are susceptible to the different antibiotics in the white pills. The bacteria in the right petri dish are resistant to most of the antibiotics in the pills; Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
These antibiotic resistant bacteria are very dangerous as it is left up to the immune system to fight them and for people that have weaker immune systems this can be dangerous or even lethal.
Bacteria Species Mycobacterium Tuberculosis; Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
While the outlook might look grim for the future of antibiotics there has been a recent study published that reports on finding a new antibiotic, teixobactin, and new possibilities for culturing microorganisms to find new antibiotics. While the discovery of a new antibiotic is an incredible achievement by itself the scientific implications in their tests against two species of bacteria in which they found no resistance to the new antibiotic is massive. In addition to the current lack of resistance to teixobactin the researchers report that the properties of the new antibiotic suggest that resistance is unlikely to develop against it as it acts on a structure of the bacteria that is highly unlikely to change due to its specific functionality of the bacteria’s life cycle.
Teixobactin was found by examining uncultured bacteria. Uncultured bacteria, which are bacteria that have yet to be grown in a lab, make up most of the population of bacteria on the planet and are a huge potential source for future antibiotics. The study reports on developing new ways to successfully culture these previously uncultured bacteria and this is highly significant as it opens doors to discovering more antibiotics that do not have resistance developed against them yet.
With this discovery the research field of antibiotics might be rejuvenated as new populations of bacteria are now able to be grown due to the new methods of culturing previously uncultured bacteria developed in the study. In the future be on the lookout for teixobactin because it might be the answer to a dangerous bacterial infection that affects you.
– Matthew Leupold
