Gradual exodus of young people towards WhatsApp, WeChat and KakaoTalk is just as their mums and dads get the hang of social networking:
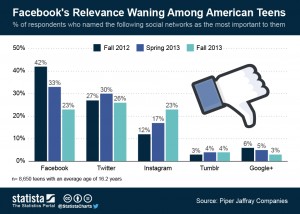
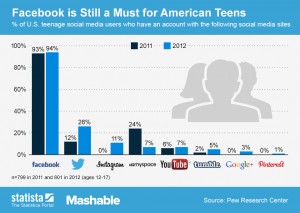
Parmy Olson, The Observer, November 10, 2013– Facebook made a startling admission in its earnings announcement this month: it was seeing a “decrease in daily users, specifically among teens”. In other words, teenagers are still on Facebook; they’re just not using it as much as they did. It was a landmark statement, since teens are the demographic who often point the rest of us towards the next big thing.
Their gradual exodus to messaging apps such as WhatsApp, WeChat and KakaoTalk boils down to Facebook becoming a victim of its own success. The road to gaining nearly 1.2 billion monthly active users has seen the mums, dads, aunts and uncles of the generation who pioneered Facebook join it too, spamming their walls with inspirational quotes and images of cute animals, and (shock, horror) commenting on their kids’ photos. No surprise, then, that Facebook is no longer a place for uninhibited status updates about pub antics, but an obligatory communication tool that younger people maintain because everyone else does.
All the fun stuff is happening elsewhere. On their mobiles.
When mobile messaging apps such as WhatsApp first emerged in 2009, they looked like a threat to mobile carriers. Everyone from Vodafone to Dutch operator KPN was mentioning them in sales calls. Mobile operators are estimated to have lost $23bn in SMS revenue in 2012 due to messaging apps, which host free instant messages through a phone’s data connection, which these days is often unlimited. Now these apps are becoming a threat to established social networks too.
WhatsApp, the most popular messaging app in the UK and on half the country’s iPhones, according to Mobile Marketing Magazine, has more than 350 million monthly active users globally. That makes it the biggest messaging app in the world by users, with even more active users thansocial media darling Twitter, which counts 218 million. About 90% of the population of Brazil uses messaging apps, three-quarters of Russians, and half of Britons, according to mobile consultancy Tyntec. WhatsApp alone is on more than 95% of all smartphones in Spain. The power users and early adopters of these apps, the ones you’re most likely to see tapping their thumbs over a tiny screen, are under 25.
Part of the reason is that gradual encroachment of the grey-haired ones on Facebook. Another is what messaging apps have to offer: private chatting with people you are friends with in real life. Instead of passively stalking people you barely know on Facebook, messaging apps promote dynamic real-time chatting with different groups of real-life friends, real life because to connect with them on these apps you will typically already have their mobile number. The trend flies in the face of recurring criticism of young people – that their social lives are largely virtual – when many more are in fact embracing the virtues of privacy and services like WhatsApp, which shun advertising.
“I only use WhatsApp to communicate and send pics these days,” said Natalie West, a twentysomething financial sales associate in London. In the last few years she has used Facebook less and less because she doesn’t want “the whole world to know” what she’s doing. When people set up events and get-togethers on Facebook, West and her boyfriend tend to reply on WhatsApp instead because “it’s more personal”. For similar reasons, some 78% of teenagers and young people use mobile messengers to plan a meet-up with friends, according to research advisory firm mobileYouth.
Another factor is the rise of the selfie, often silly self-portraits taken at arm’s length with a mobile. Almost half of the photos on Instagram feeds among people aged 14 to 21 in the UK are selfies, according to mobileYouth. Sending those photos via a mobile messaging service is safer than broadcasting them on Facebook, since they’re less likely to be seen by a boss or dozens of Facebook friends you forgot you had. Selfies are even bigger on Snapchat, the evanescent photo sharing app that deletes a photo several seconds after it has been viewed. With about 5 million active monthly users, the service has inevitably become a favoured way for teens to send sexy or even naked photos of themselves, an ill-advised practice known as “sexting”. But teens also love Snapchat because it allows them to send inane photos of themselves without fear of leaving a permanent digital footprint.The California-based app is seen as so hot, with so much potential for growth, that it has already been pegged with a $2-$4bn valuation in the Silicon Valley tech community. Estimates are even higher for WhatsApp, which makes money through an annual subscription; some observers suggest it could be worth $5bn or more.
The final, big reason why young people are gravitating towards messaging apps is that many of these apps no longer do just messaging. They are social networks. The best examples come out of Asia, with messaging platforms KakaoTalk (South Korea), WeChat (China) and LINE (Japan). All have tens of millions of users, with WeChat boasting more than 200 million, and take their services beyond offering straight messaging to games, stickers and music sharing. Before you write off digital stickers as inane, they are a decent moneyspinner for LINE: of the $58m the company made in sales in the first quarter of 2013, half came from selling games and 30%, or roughly $17m, from sales of its 8,000 different stickers. Some are free or, in Spain where LINE has 15 million registered users, cost around €1.99. Often users choose stickers instead of words when they need to express themselves, one LINE executive said; it’s known to have helped couples get over fights more easily by offering multiple stickers to say sorry.
Read More: The Observer

 Follow
Follow
