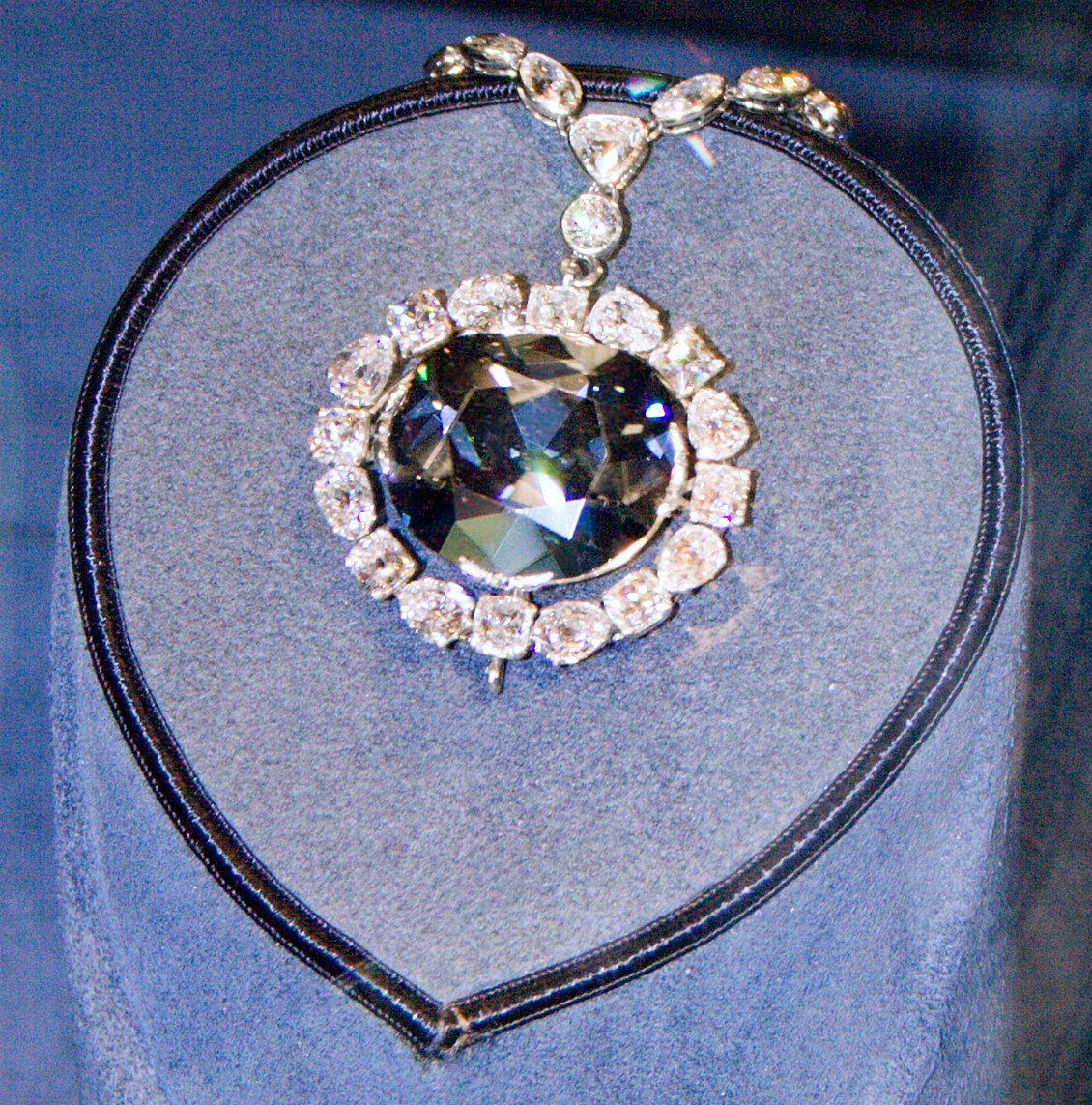
Hope Diamond, which is on display at the Smithsonian Museum, is a famous Type 2 Diamond which weighs 45.42 carats/ 9.1 grams. (Source: Wikimedia commons)
Diamonds can be categorized according to their compositions. The categorization of diamonds is actually quite simple, as there are only 2 types of diamonds: Type I and Type II. Type I diamonds are the most common type and are categorized as such for their nitrogen impurities. Type II diamonds, on the other hand, contain no nitrogen at all. It’s this rare type of diamond that interests Evan Smith, a Ph.D student at UBC. In his paper, “Implications of Metallic Iron and Nitrogen in the Sublithospheric Mantle,” he examines the factors that may account for the lack of nitrogen in Type II diamonds.
Type II diamonds are categorized into Type IIa and Type IIb diamonds. Type IIa diamonds have little to no amounts of any kinds of impurities while Type IIb, the rarest type of them all, contain large amounts of boron (another impurity).

Daria-i-Noor, a type 2 diamond, from Iran which weighs 186 carats/ 37.2 grams is owned and passed down through regents of the Mughal empire.
(Source: Wikimedia Commons)
In contrast, Type I diamonds are further subcategorized into Type IaA and IaB, according to how the nitrogen atoms are grouped within the carbon lattice of the diamond. An additional Type I categorization, Type Ib, exists for diamonds that contain nitrogen but so little of it that the atoms are isolated throughout the diamond, rather than grouped together like in Type Ia diamonds.
It is possible to tell what kinds of impurities are present in diamonds by their colour, as impurities dictate what wavelengths of light a diamond can and cannot absorb. An impurity-free diamond (Type IIa) is perfectly colourless. Diamonds with trace amounts of an impurity appear colourless, but these impurities can easily be measured using infrared spectroscopy.

Beau Sancy is a type 2 diamond which weighs 55.23 carats/ 11 grams and was sold in 2012 for $9.57 million. (Source: Wikimedia Commons)
Clear white diamonds, Type II diamonds, are the way they are because of their lack of impurities: they’re usually what we visualize when we think of diamonds. They also top the lists of the most famous and valuable diamonds worldwide. The most renowned example is the Cullinan I, the largest cut diamond in the world. This diamond was cut into several pieces and in encased in the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom.
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
~Anupreet Sihra, Nicholas Macdonald and Adil Cader.