A new study by Howard J. Federoff and his team of researchers has been released, and they have discovered a new way of identifying people who are at risk of having Alzheimer or other mental brain impairments within three years. This five year study took place at Georgetown University Medical center, and the study states that their discovery is capable of predicting the presence of the disease with 90% accuracy, by identifying ten specific lipids (fats) in your blood that are believed to present disease onset.
Alzheimer is a life altering degenerative disease that is one of the more common types of dementia, a loss of cognitive ability, and it is affecting an estimated 40 million people worldwide, with the World Health Organization stating that the number will double every 20 years. By 2050, the numbers are expected to rise to over 115 million, a staggering number for something with no cure.
But our current way of predicting Alzheimer is not useful in preventing or treating the disease. At this time, Alzheimer is typically diagnosed when the various symptoms of Alzheimer starts showing up, such as memory loss. However, this comes at a time where there is already irreversible damage to the brain, and as there is presently no cure, the damage is already done. Although there are various drugs presently available to try and combat these effects, they have all failed and Federoff believes this is due to the drugs being used far too late into the disease timeline.
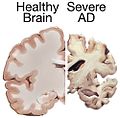
Comparison of a normal brain and one with Alzheimer’s.
Photo by: National Institutes of Health (Source: Wikimedia Commons)
However, this study gives us a cheap and effective basis for diagnosing the disease, so while it only predicts with 90% accuracy, this is an improvement over the previous method of waiting for the first stages of the disease. Howard J. Federoff explained “We consider our results a major step towards the commercialization of a preclinical disease biomarker test that could be useful for large-scale screening to identify at risk individuals”.
Although this method is not clinically ready yet, this study is a step in the right direction of finding an effective way to combat Alzheimer.
Here is a link to the original study:
http://www.nature.com/nm/journal/vaop/ncurrent/abs/nm.3466.html
-Jeffrey Chen






