Today, Ebola Virus in West Africa is the world’s most dangerous disease in this year. World Health Organization has declared an international health emergency as more than 2,100 people have died of the virus in Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone and Nigeria in this year.
What is Ebola Virus?
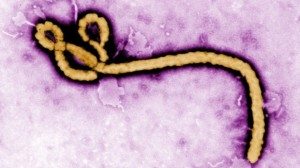
Ebola is a viral illness that the initial symptoms are sudden fever, intense weakness, muscle pain and a sore throat. Also subsequent stages are vomiting, diarrhea. Furthermore, some people with Ebola virus have both internal and external bleeding.
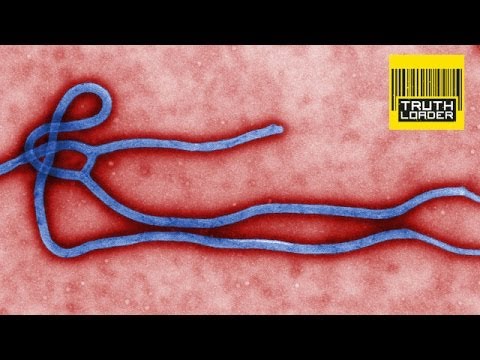
The current outbreak in west Africa is the largest and most complex Ebola outbreak since the Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976. It has also spread between countries starting in Guinea then spreading across to all the nations.
How Ebola Virus spreads?
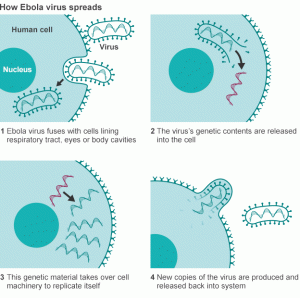
The fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are natural Ebola virus hosts. Ebola is transmitted into the people through the physical contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other fluids of infected animals like chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, or monkeys. They were ill or dead or in the rainforest.
Health-care workers also have been infected when they treated patients with EVD. This has occurred through close contact with patients when infection control are not strictly practiced.
People remain infectious as long as their blood and fluids, including semen and breast milk, contain the virus. Also People who have recovered from the disease can still transmit the virus through their semen for up to 7 weeks after recovery from illness.
Treatment and vaccines
There is as yet no proven treatment available for EVD. The reason is that this virus is mutated all the time. Therefore, there is not a 100% clear vaccine for all the people. However, a range of potential treatments including blood products, immune therapies and drug therapies are currently being studied. There is no any perfect vaccines are available yet, but 2 potential vaccines are undergoing human safety testing.

One response to “Why Ebola is so dangerous”