Everyone has used for super glue at least once when fixing a broken object. This plastic glue was not only used for the quick fix but also a medical product that saved lots of patients on the battlefield. Moreover, the interesting fact that reported by The Newyork Times, is that today professional athletes also use the super glue to seal their shallow cuts.
Great accidental invention: “Super glue”

Credit: cbsnews.org
Super glue, that is a chemical compound, was accidentally invented by Dr Harry Coover in 1942. During World war 2, he was working on making clear plastic lenses to precise gun sights for soldiers. Unfortunately, cyanoacrylate(CA) was excluded as a material since it was extremely sticky. However, after 6 years, he realized that this chemical permanently glues anything. This chemical, CA, is what we know as super glue.
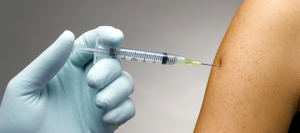
Fast way to stop bleeding: “Super glue”

Credit: Simple History
Dr Coover studied how to hold human muscle tissue together with the possibility of CA being used for medical purpose, and in 1964 he applied to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the CA for medical use. While not yet approved because of potential toxicity, spray type of CA was used as a temporary treatment in the Vietnam War, to seal soldiers’ wounds to preventing bleeding, and many lives were saved.
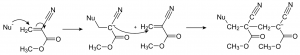
Properties of “Super Glue”
Credit: Wikipedia
The main ingredient in super glue is cyanoacrylate which is clear gel-like liquid. CA is acrylic resin rapidly polymerized when it reacts with hydrogen that is represented as ‘Nu+’ in the picture. When its exposure in presence of water, then it makes stronger and longer chain which is called poly-cyanoacrylate. Through this reaction, it transforms from liquid to solid, from the surface to deep inside. Due to humidity in the air, it can also explain why the glue harden when you forget to close the cap after use it.
Safe medical glue for surgery
Super glue is considered dangerous to use on serious wounds such as deep cuts to two main side effects:
- Curing is an exothermic reaction which releases heat; it could cause damage to surrounding tissues.
- This curing process creates CA and formaldehyde, which irritate eye, skin and respiratory.
The original super glue is not allowed to use to heal the cuts officially. But there is an alternative that was invented for a medical purpose. In 1998, FDA approved a 2-octyl-cyanoacrylate, an improved medical adhesive that was less irritating. As commercializing this new safer medical adhesive, we can expect fast recovery without stitching.
Written by Anna Kwon