UNCED Statement of Forest Principles: The term Sustainable Forest Management [SFM] can be traced to the Forest Principles and Chapter 11 of Agenda 21 of the UNCED Rio 1992. The guiding objective of the Forest Principles is to contribute to the management, conservation, and sustainable development of all types of forests, and to provide for their multiple and complementary functions and uses. Principle 2b specifically states that:
“Forest resources and forest lands should be sustainably managed to meet the social, economic, ecological, cultural, and spiritual human needs of present and future generation.”
The concept of SFM has continued to evolve since UNCED Rio 1992 through the international forest policy dialogues within IPF, IFF, and UNFF and through a large number of country-led and eco-regional initiatives, e.g. FAO, ITTO, UNEP.
What is Sustainable Forest Management [SFM]?
[ITTO]: “Is the process of managing forest land to achieve one or more clearly specified objectives of management without undue reduction of its inherent values and future productivity or undesirable effects on the physical and social environment.”
[Canadian]: “The maintenance and enhancement of the long term health of forest ecosystems, for the benefit of all living things while providing environmental, economic, social and cultural opportunities for the benefit of present and future generations.”
[American Forest and Paper Association]: “Sustainable forestry means managing our forest to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs by practising a land stewardship ethic which integrates the growing, nurturing and harvesting of trees for useful products with the conservation of soil, air and water quality, and wildlife and fish habitat.”
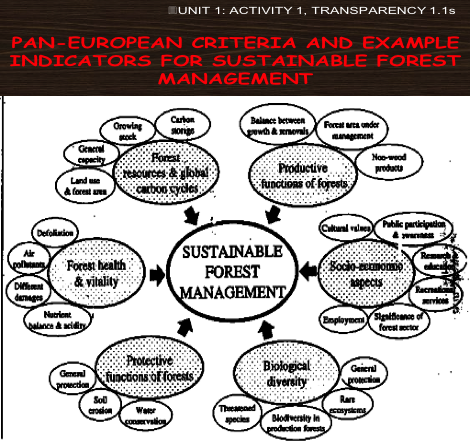
Overall, SFM is difficult to explicitly define. However, several recent international meetings have suggested the following (6+1) thematic elements are key components and may be used as a reporting framework on SFM (success and failure):
- Extent of forest resources;
- Biological functions;
- Forest health and vitality;
- Productive functions of forest resources;
- Protective functions of forest resources;
- Socio-economic functions; and
- Legal, policy, and institutional framework (which transcends the above 6 elements).
Read and understand the following presentation:
Brief Description and Number of Countries Participating in the Major International On-going Processes on Criteria and Indicators for Sustainable Forest Management.
Open the pdf file in new window here
Holmgren, M. L. & Castaneda, F. (2003). Sustainable forest management and the ecosystem approach: two concepts, one goal. Working Paper FM 25, Forest Resources Development Service, Forest Resources Division, FAO Rome.
Open the pdf file in new window here
Please answer the following self-reflection question. After formulating your answer, you may post it online at the Knowledge Café for this course as a way to share your ideas and glean knowledge from other students’ responses.
SrQ#2. 1: Can you list down 2 or 3 each of successes and failures of UNCED Rio 1992?