If someone suffered a heart attack or was involved in a car accident, the first place we would turn to is the nearest hospital, right? It happens almost every day; someone is carried into the ER on a stretcher and leaves smiling, walking on their own two feet. Generally, hospitals are perceived to be a safe place of medical assistance, treatment, and recovery, however, there is growing data to suggest that a stay in the hospital may actually come with risk.
Health care-associated infections (HAI), also called nosocomial infections (from the Greek word nosokomeíon, meaning hospital), are classified as infections that occur during a hospital admission and up to 3 days after discharge. They are a growing cause of lengthened hospital stays, medical complications, and even death in patients. In fact, it is estimated that these infections rack up a cost of one billion pounds for England’s National Health Service and over $35 billion for U.S. hospitals.
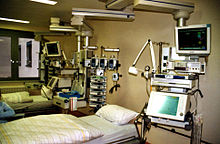
The intensive care unit (ICU) has one of the highest HAI rates.
Courtesy of Wiki Commons
In 2011, the United States had almost 722,000 cases of HAI, ranging from surgical site infections to pneumonia. The Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program also found an increase in the incidence of a specific bacterium, called C. difficile, from around 42 cases per 100,000 in 1992 to 160 per 100,000 in 2003. Additionally, the severity and reoccurrence also spiked, with more severe outcomes recorded, including perforated large intestines, shock, and death.
A common misconception is that only the elderly are at risk for HAI due to their weaker state of health. This is untrue, as studies find increasing numbers of these infections in children’s hospitals, maternity wards, and in the young adult population. A study published in 2014 found a more than triple increase in incidence of flesh eating disease, known as necrotizing fasciitis, in pregnant women that were admitted to hospital for delivery over the past decade. Children also experience a high prevalence of HAI, with the highest percentages recorded in intensive care (19%) and transplant units (27%).
So what can be done?
Unsurprisingly, poor hand washing has been attributed to 40% of infection transfers in hospitals, thus focusing on improving hand hygiene habits can have a positive impact. Increasing compliance of wearing protective accessories including gloves, masks, and aprons is also critical. As well, creating a system that immediately isolates patients who have contracted a severe infection is key to prevent further spreading.
Careful attention to sanitation must also be emphasized, as it was found that an antibiotic-resistant bacteria that attacks the intestinal tract can also be transferred between patients through the use of thermometers.
The issue of HAI is a global problem, however it is not all doom and gloom when it comes to the future of patients’ well-being. Much research is currently underway to find new methods to decrease the prevalence. Take a look at the video below from the Mayo Clinic, where they tested the effectiveness of UV light disinfection. They found an impressive 30% decline in C. difficile infection in the UV-treated rooms!

Kerrie Tsigounis