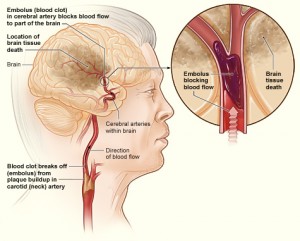
Passwords are the most common authentication method we use today to prove one’s identity. One of the major problems with using passwords is that people are often faced with a trade-off between security and usability; people are either making their passwords too simple, and are easily hacked into, or are making them extremely complicated to remember.
In general, compared to other existing authentication systems, such as digital signature and fingerprint recognition, passwords are cheap and simple to use. Therefore, it is the most widely used authentication mechanism today. Recently, something possibly “better” than passwords has arrived. A paper that was published on PeerJ proposed a new authentication system called “Facelock” based on the facial recognition technology. See the following YouTube video for a short introduction of facial recognition.

The physiological principle behind this new authentication system is that our brains have the ability to recognize familiar faces. You can easily recognize many different faces of the same person who you know pretty well, but you may find it is difficult to identify strangers across a range of images. Facelock is built on the fact that only authentic users can reliably identify the target faces but attackers are unlikely to recognize them. When logging in, Facelock allows users to go through a series of pages that each contains nine faces of different people with only one face that is familiar to the account holder. To unlock your account, you need to successfully select the target face on each page.

Can you recognize the person who appears twice in the image? Image from http://theconversation.com/us
However, such a system also has certain limitations. The system is vulnerable to an attacker who has many friends in common with the user, which means your closest acquaintances are likely to be able to recognize your target faces. Additionally, if the target person whose appearance is distinctive (i.e. has an outstanding characteristics such as a full beard or have a bald head) or if the images of the same person are not sufficiently different, then an attacker may still be able to identify the target faces without many challenges. On the other hand, there is no boundary to determine whether the image is distinctive or not and it is hard to tell if the two images are different enough. So how should we select the images for the system to avoid similarity and distinctiveness? Finally, Does Facelock actually benefit to a user when compared to the password authentication system? In fact, Facelock is not as easy to use as passwords and it takes more time to unlock your account because you have to spend more time recognizing faces.
In conclusion, this new authentication system seems reliable and implementable with current technology, but to make it a viable replacement of passwords, the developers should pay attention on how to make appropriate target selection to make it more user-friendly.
Ying Yu