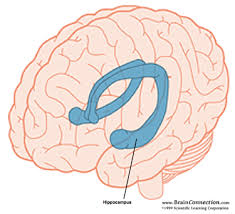
‘Getting a buzz’, ‘getting trashed’, or ‘getting wasted’ are all phrases we have heard one time or another, most likely during our later high school years and first year of university. We are told time and time again that adolescent drinking is bad for one’s own health and safety, but not just by our parents, but scientists as well. A recent study done in Spain where researchers looked at the brains of unconscious mice to see what the effects that alcohol consumption had on different parts of their brain. The results were a decreased amount of brain activity in the rodents’ areas around their hippocampus. The scientists also looked deceased-human brains of people that were alcoholics in the past and found that habitual exposure and ingestion of alcohol led to increased degradation of specialized connection between brain cells and the extracellular matrix of these cells.
However, binge or heavy drinking might not only affect the drinker in the present, but might affect their future kids as well especially if the drinker is still an adolescent. A group of researchers in the United States used adolescent rats to test whether heavy drinking patterns affected DNA methylation, the process that CH4 molecules are added to DNA, in the rats’ offspring. The animals mated 24 hours after receiving the last alcohol administration and the offspring were produced. The researchers examined the genes in the hypothalamus which is the region of the brain responsible for the regulation of hormones that control various things like hunger, thirst, and body temperature. There were differences in the DNA methylation of the rats with alcohol-induced parents versus those who’s parents were not induced with alcohol.
Toni R. Pak, PhD, one of the authors of the paper of the study said “Adolescent binge drinking not only is dangerous to the brain development of teenagers, but may impact the brains of their children.” The findings were from an animal-model study and do not necessarily translate to humans entirely, but the animal model, namely the rats, and humans share many biological similarities such as our means of breaking down alcohol and functions of the hypothalamus. Therefore you should still be careful about drinking large amounts of alcohol at once because you are not only risking having a bad hangover the next morning, but possibly endangering the your future children’s DNA and being.





/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/7221875/Screen%20Shot%202016-10-05%20at%206.36.46%20AM.png)