Space missions begin long before lift-off, and continue after their conclusions as well. In preparation for the first human Journey to Mars, the European Space Agency (ESA) and Russia’s space agency Roscosmos jointly sent the latest of landers to Mars as part of their ExoMars programme. On March 14, 2016, Schiaparelli EDM Lander was jettisoned into the cosmos with the goal landing on Mars to test technology that may be used in future Mars missions and collect data on the Red Planet. The lander is named after famed Italian astronomer, Giovanni Schiaparelli, whose biggest contributions to science are his telescopic observations of Mars. During his initial observations, he named various seas and continents on the planet.
The acronym “EDM” in the lander’s official title stands for Entry, Descent, and Landing Demonstrator Module indicating that the lander’s main purpose is to test soft-landing technology that the ESA and Roscosmos intend to implement during part to of the ExoMars programme where they will attempt to land a rover on the planet. Note that landers are stationary, while rovers are mobile vehicles.
When Schiaparelli lander’s attempted descent on October 19, 2016, didn’t go as planned, many touted that the mission was failure, but I don’t believe that’s necessarily the case. The lander disembarked from an orbiting carrying vessel on October 16, three days before its descent. A few hours before the planned landing, however, its signal was lost. ESA’s Mars Express orbiter and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and MAVEN probe all listened intently for signals from the lost lander. Data retrieved from the lander before the accident suggest that its landing parachute and rocket thrusters both failed to execute properly.
A brief account of how Schiaparelli‘s descent was supposed to occur and what actually happened from The Cosmos News:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=McSCXWpZT8k
NASA’s MRO later returned images of the crash site.
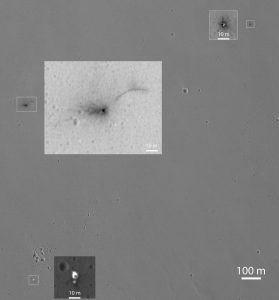
Area where Europe’s Schiaparelli Lander crashed on Mars, with 3 magnified sites where space craft parts hit the ground.
http://www.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/thumbnails/image/pia21131-hirise_of_edm.jpg
While the Schiaparelli lander did not effectively land on Mars, the mission is still a success because it fulfilled its goal of testing the landing equipment and returned enough data to Earth for part 2 of the ExoMars programme to proceed as planned.
Navpreet Ganda
