Physarum polycephalum, literally the “many-headed slime”
You may have spotted these yellow slime mold in your backyard, they flourish in shady, moist areas, such as decaying leaves. It is a single-celled organism that is not an animal, plant nor fungus. Scientists classify them to the taxonomic group named Protist, which is a group of organisms that are unicellular or unicellular-colonial and form no tissues. Slime mold isn’t capable of forming tissues, let alone organs or body systems. But surprisingly, a group of scientists from Japan found the brainless slime mold, Physarum polycephalum, to be able to remember, decide and solve complex optimization problems.
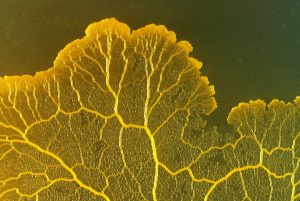
A group of researchers led by Toshiyuki Nakagaki from the Hokkaido University in Japan, placed Physarum polycephalum in a petri-dish scattered with oat flakes. The position of food scraps was deliberately placed to replicate the locations of some of the most visited site in Tokyo. In the first few hours, the slime mold’s size grew exponentially, and it branched out through the entire edible map. Within a few days, the size of its branches started to shrink, and the slime mold established a complex branching network between the oats on the petri-dish. Despite growing and expanding without a central coordination system like the brain, the mould had re-created an interconnected network made of slimes that looks almost exactly like the efficient, well-designed Tokyo subway system.
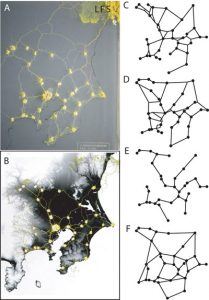
Comparison of the Physarum branching networks with the Tokyo subway networks
As you may know, the Tokyo’s rail system is one of the best in the world. With 102 train lines, it serves an estimated 14 billion passengers per year. Such a legendary metro system is the fruit of collaboration between community dwellings, civil engineering, urban planning over decades. However, the lowly slime mold solve this complex spatial problem in a matter of just a few days.

A beautiful map of the complex Tokyo subway system
Slime mold has been evolving on our planet for an estimation of at least 600 million years, and has survived through countless rounds of evolutionary competition. If we could capture the essence of this ancient adaptive network formation system and summarize it in to engineering and biological models, it will certainly inspire new algorithms that guides network construction many domains.
—-Ran Bi