Cancer is the reality that haunts the forefront of society’s mind and one of the greatest killers that we fear today. It comes as no surprise that we would expect a great deal of research to be invested in its prevention. When researchers are looking into every possible opportunity that may yield a solution, it peaks our curiosity that a bizarre animal such as the naked mole rat may hold the key.
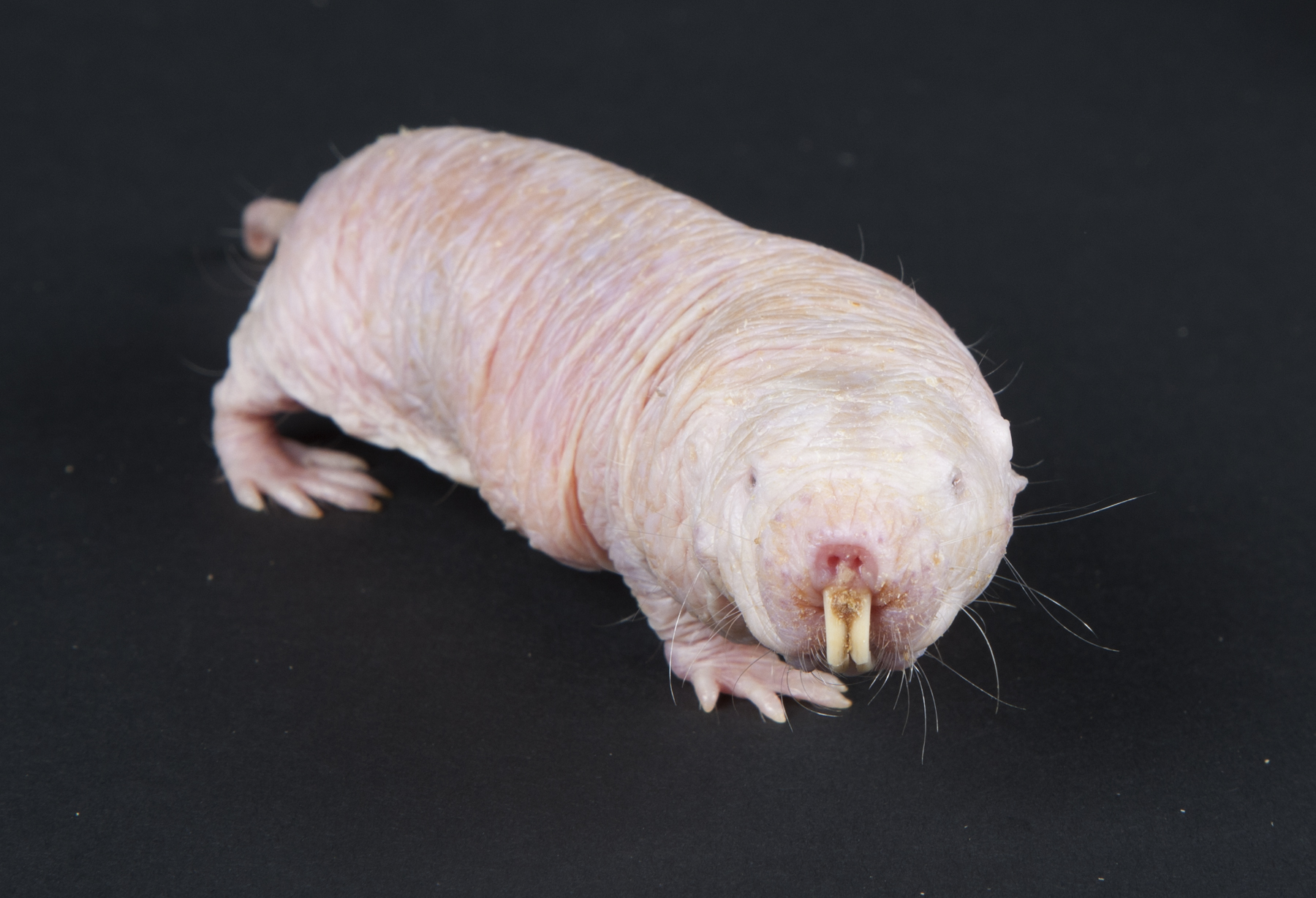
The Naked Mole Rat (Source: Flickr.com)
Although this not very visually appealing creature doesn’t seem to stand a chance against something as notorious as cancer, scientists at the University of Haifa in Israel believe that the cells of these mole rats secrete a substance that could be linked to the prevention of cancer. In addition to this the naked mole rat lives for a much longer period than your conventional species of rats, up to around thirty years, and hasn’t yet been detected to have any form of tumours. These features of this animal allowed it to win vertebrate of the year in the science magazine.
So how does this seemingly insignificant animal keep cancer out? Scientists from the University of Rochester in New York along with scientists from The University of Haifa in Israel have suggested that the substance responsible is a super sugar called high-molecular-mass Hyaluronan (HMM-HA). The proposed mechanism is that when secreted by cells it decreases cell overcrowding and the formation of tumours. This substance is also secreted by humans into the extracellular matrix of cells, but the sugar in these rats are ‘much heavier’. The evolution of these rats deep underground may have lead to the formation of this advanced version of the sugar. Additionally, this sugar secreted by mole rats allows their skin to be very much more elastic.
Research conducted on these creatures include, inducing cancers via carcinogens on them, however, it was found that the mole rats didn’t appear to develop any tumours. This differs from an experiment in which the mole rats were exposed to these same carcinogens in the absence of the secreted sugar (Hyaluronan). In this case, tumours developed, which lead researchers in the direction that this was, in fact, the substance responsible for the mole rats cancer free record.
The research into this substance is still progressing slowly, like all things in science and medicine. There are still several problems that researchers face, such as; how can it be harnessed and administered to humans? Will the substance cure already existing tumours and how can this be tested safely? Unfortunately several news articles that have been published are misleading to people who are looking for current cancer treatment as this research is in no way a current treatment and still needs several years of work to be of substantial use for human applications. That being said it is a significant door that has been opened in the field of cancer research and should be pursued.
~Adil Cader.