The blood-brain barrier is a protective covering that surrounds the brain and prevents contaminants, pathogens and other toxins from entering the brain. Sounds amazing, right? Yes! It’s the brain’s own defence mechanism to protect itself, however it can come in the way when trying to treat brain disorders like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s or even brain tumours.
Well, the problem is that the barrier only allows certain molecules such as water, glucose, lipid soluble molecules and some gases to pass and enter the brain. When designing drugs to combat brain diseases, researchers must find ways to bypass the blood-brain barrier which isn’t as easy as it seems. The cells that make up the barrier are tightly clustered together making it nearly impossible for drugs to enter into the brain.
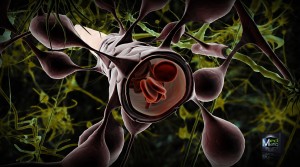
In order to overcome this problem, researchers in Toronto designed a technique that was a breakthrough in breaking the blood-brain barrier. The technique, which has not yet been named, is currently being tested on patients with brain tumours. The first step in this technique is to administer a dose of a chemotherapy drug and also inject the patient with microbubbles which are smaller than red blood cells. The microbubbles and drug travel to the brain and come face to face with the blood-brain barrier. The patient is then placed in an MRI machine and the exact location of the tumour is identified. Once the tumour has been located, ultrasound waves are emitted to that specific region causing the microbubbles to vibrate really fast.
Courtesy of Newswise
These vibrations cause the tight junctions of the cells that make up the blood-brain barrier to loosen up, creating a small passage for drugs to pass through. Once the ultrasound waves stop, the microbubbles are reabsorbed by the lungs and the passage which forms closes within a six to twelve-hour window.
Current techniques being used to penetrate the blood-brain barrier are invasive and not as targeted as this technique. If researchers can find a way to bypass the blood-brain barrier in a non-invasive manner, it will change therapeutic approaches to treating brain disorders. Like any other procedure which involves opening the blood-brain barrier, there are risks associated with this technique as well. The blood-brain barrier remains open for several hours after the initial procedure is done and during this time toxins and other contaminants can enter the brain through that passage. This technique is currently undergoing clinical trials but if it proves to be effective it can revolutionize the way we treat brain diseases.
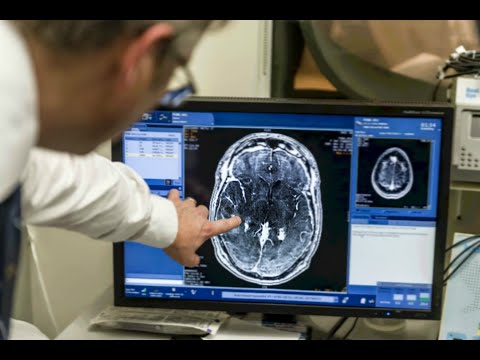 Courtesy of Sunnybrook Hospital
Courtesy of Sunnybrook Hospital
Harnoor Shoker







![http://www.nasa.gov/centers/glenn/shuttlestation/station/microgex.html [Micro-gravity in Space]](https://blogs.ubc.ca/communicatingscience2015w211/files/2016/01/601194main_kc135-microgravity-training-300x173.jpg)