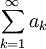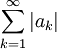[previous] [next]
The ratio test requires the idea of absolute convergence. Given any infinite series Σak, we can introduce the corresponding series
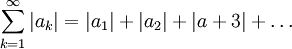
whose terms are the absolute values of the original series. We can explore whether this corresponding series converges, leading us to the following definition.
| Definition: Absolute Convergence |
|---|
| The infinite series
is absolutely convergent if the series of absolute values
is convergent. |
A few simple examples demonstrate the concept of absolute convergence.
Example: Convergent p-Series
The infinite series
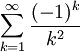
is absolutely convergent because
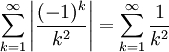
is a convergent p-series (p =2).
Example: Harmonic Series
The infinite series
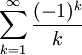
is convergent (by the alternating series test), but is not absolutely convergent because
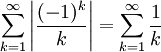
is the infamous harmonic series, which is not a convergent series.
It is possible for a series to be convergent, but not absolutely convergent (such series are termed conditionally convergent, but we do not need this definition for our purposes).
[previous] [next]