Background Information:
Did you know that the use of artificial light has potentially contributed to reduced plant populations as well as world hunger?
A study done by researchers at the University of Zurich found that artificial light tends to greatly reduce the vector pollination rate of various plant species by nocturnal and even diurnal insects. Interestingly, there have been observed cases where artificial light actually increased the vector pollination rate of some plants for unknown reasons. However, the first case is much more common.
How Vector Pollination Occurs:
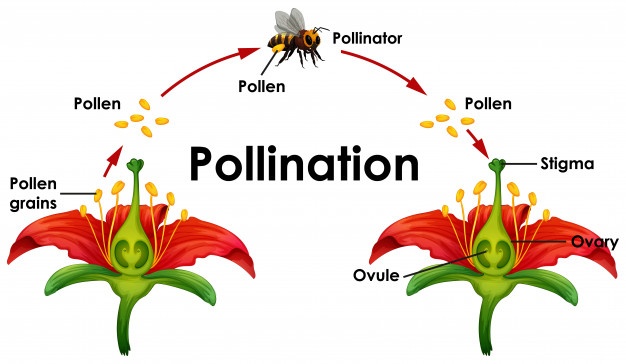
Credit: ScienceDirect. Downloaded from: Unsplash.com
Plant Reproduction:
The implications of reduced vector pollination of plants due to artificial light are still not fully understood, however, an article by Chrissy Sexton (2021) touches upon possible reasons why this occurs. It is explained that artificial light causes ecological disruptions which are mainly linked to reduced nighttime vector pollination of plants as there are alterations in species interactions, the behavior of insects, and even mortality. Due to the decreased pollination of various plants, they are not able to reproduce as frequently which can cause species endangerment and loss of genetic variation. This is of major concern as both species endangerment and loss of genetic variation are catalysts for species extinction.
World hunger
World hunger is a very complicated matter as various sources can contribute to the loss of food like mismanagement of food, expiration of food, and most importantly, weather events such as droughts. Remarkably, the use of artificial lights has been found to indirectly contribute to food shortages as it generally leads to a decrease in insect pollination of plants and crops. This means that there is a decrease in food produced. These findings are concerning as with the atmospheric CO2 levels continually rising at an unimaginable pace (shown in the graph below), global warming will continue to cause more and more droughts, leading to greater destruction of crops and further reducing the world’s food supply.

Credit: GlobalChange. Downloaded from: Unsplash.com
What’s next?
A significant problem that arises when considering the conclusions of this study is that artificial light is expected to continue expanding in its use at about 2-6% per year. Thus, it is pivotal that this problem is addressed sooner rather than later to limit the reduction in the global food supply, as there are already a plethora of other things influencing food supply. As there is not enough research on the topic, there are no current definitive solutions to eliminate the negative effects of artificial light on vector pollination. However, some efforts can be taken to minimize the loss of food and decreased reproduction of various plant species due to artificial light. These efforts include ensuring pollination of plants occur leading to reproduction by manually pollinating plants and ensuring optimal growth of crops by providing the best possible nutrients, fertilizers, and etc. Scientists hope these efforts will increase plant reproduction and crop production, allowing humans to have one less thing to worry about.
– Balkaran Dhaliwal