Did you know that an estimated one in four adults suffer from dry mouth? Unfortunately, head-and-neck cancer patients often experience the symptom of a dry mouth, otherwise known as xerostomia. Most patients with xerostomia experience damage to their parotid glands, which are located in the mouth and help with saliva production. Xerostomia is experienced by cancer patients due to radiotherapy, a type of cancer treatment, but not for much longer.
In 2020, a study led by Caleb M. Sample, a researcher at the University of British Columbia (UBC), found a solution to help treat this condition. His treatment method led to an increased amount of saliva production in the mouth, a year after patients completed radiotherapy.

Dry Mouth. Source: Accurate Clinic
What is Xerostomia?
According to Sample, when the parotid glands are hit by radiation beams to treat nearby tumors, they are damaged and can’t produce saliva anymore.
“[Xerostomia] is a result of radiation damage to the salivary glands and in particular the biggest saliva glands which … are called the parotid glands.”
Numerous symptoms may indicate impaired saliva production due to xerostomia.
The following video, “Goodbye to the Dry, New Radiotherapy to Try!”, provides an overview of xerostomia and how it can be minimized and treated.
Protecting the Parotid Glands
Is there a way to prevent xerostomia symptoms? Luckily, in 2020, Sample investigated a solution to this condition in hopes of minimizing the onset of xerostomia in head-and-neck cancer patients. Sample’s treatment plan for minimizing xerostomia involved the use of something called an optimizer to protect the important areas of the parotid gland.
In simple terms, an optimizer is a software that determines giving the most radiation to tumors and the least radiation to healthy organs. The treatment plans, created by Sample, are loaded onto the optimizer and prevent important areas of the parotid gland from receiving radiation. By protecting regions of the parotid gland that could result in a decrease in saliva if hit with radiation, cancer patients can expect healthier outcomes with a lower risk of experiencing xerostomia.
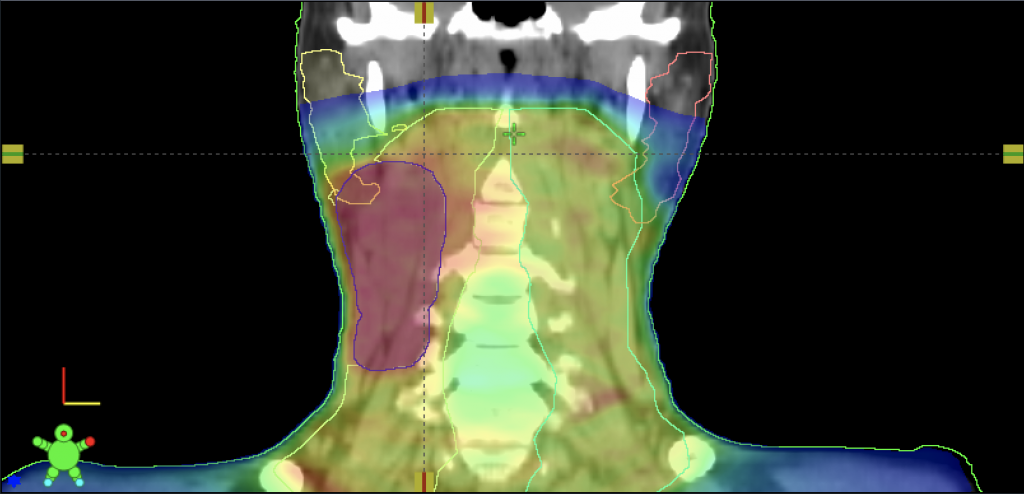
Front scan of the neck. Red shade represents a tumor. Source: Caleb Sample
Check out Parotid Party, an episode of Cancer Crushers, for more information on Caleb’s research:
Thank you to freesound.org (plasterbrain, kellieskitchen, Amazing_Brick_Movies, MrAuralization, deleted_user_2104797) for providing audio effects used throughout our podcast.
Impact of the Research
With further research opportunities, Sample’s treatment method could be applied to other organs-at-risk receiving radiotherapy, such as the liver, kidneys, and lungs. He hopes his research can be implemented into future treatment plans for radiotherapy patients to prevent oral health problems.
Overall, combating cancer through radiotherapy, only to develop further health problems, such as xerostomia, can be an exhaustive battle. Despite these difficult ordeals, Sample’s research provides hope for cancer patients and shows that we are progressing towards healthier radiotherapy treatments.

Head & Neck Cancer Ribbon. Source: Medical News Today
– Julia Shim, Tina Huynh, Ramdeep Dosanjh, Aaron Yoon


 The Great Barrier Reef, Australia.
The Great Barrier Reef, Australia.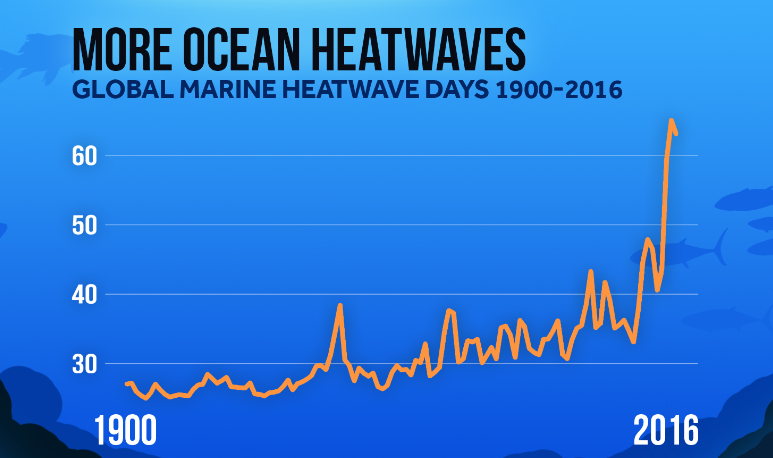 Large Recent Increases in Marine Heatwaves
Large Recent Increases in Marine Heatwaves










 Treating your Seasonal Allergies
Treating your Seasonal Allergies Examples of Seasonal Allergens
Examples of Seasonal Allergens