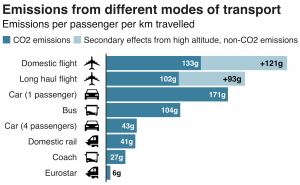
It is quite obvious by now that if we don’t change our ways of living, our planet is doomed. Due to rapid industrialization and urbanization, there is an increased amount of pollutants emitted into the atmosphere that are slowly damaging the earth. In today’s society, most of the energy production is coming from fossil fuel combustion and this is the key source of CO2 emissions to the atmosphere. The primary energy demand will continue to increase and as of right now, fossil fuels still contribute to 82% of the global demand of energy.
Source: bbc.com
An article written by Ashokkumar Veeramuthu and team describes the potential use of microalgae to produce biodiesel. You may be asking, what are microalgae and what the heck is biodiesel? Let’s jump straight into it.
What is Biodiesel?
Biodiesel is made from materials such as plant oils and animal fats. It’s an alternative to petroleum diesel and has a more favourable combustion profile as it emits much less CO, CO2 and SO2 into the atmosphere. Since we are slowly killing our planet, replacing our non-renewable energy sources with green alternative sources doesn’t sound like a bad idea.
Why Use Microalgae?
You may be wondering, what is so special about microalgae? Why can’t we use some type of terrestrial plant like corn to produce biodiesel? Studies show that the use of microalgae is the best option for the production of a renewable and sustainable source of energy. Microalgae are unicellular photosynthetic organisms living in aqueous environments that convert sunlight, water and CO2 into algal biomass. The reason why there has been a shift of attention towards microalgae to produce biodiesel is because microalgae provide a large range of advantages compared to terrestrial plants. The benefits of microalgae include high lipid concentrations (which can easily be converted to biodiesel through a process called transesterification), rapid growth and minimal nutrient requirements. The table below compares values of the biodiesel productivity of microalgae and other plants.
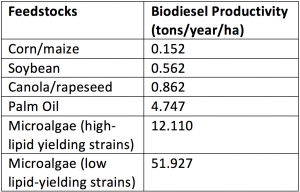
Amount of biodiesel productivity for different feedstocks. Source: intechopen.com
Microalgae also tend to grow 10 times more rapidly than terrestrial plants and less than a tenth amount of land is required to produce the same amount of biomass. Additionally, microalgae don’t require immense amount of fertilizers to grow unlike terrestrial plants. The cultivation of microalgae can be carried out by using wastewater, since it is rich in key nutrients. Furthermore, the use of wastewater decreases costs of cultivation greatly and makes biodiesel production commercially viable.
This video showcases the whole process in a nutshell:
Source: David T. Kearns (YouTube)
In today’s world, there’s a shift of attention to deal with the issue of climate change. From Elon Musk creating fully electric vehicles to Joe Biden rejoining the Paris climate accord within hours into presidency, we as humans are finally taking initiative to save our planet. The future of creating fuels from microalgae sounds promising and having a range of renewable sources of green energy will be beneficial to us in the coming time.
– Parwaz Gill


 Abbott’s ID Now COVID-19 Test
Abbott’s ID Now COVID-19 Test A Typical Nasal Swab
A Typical Nasal Swab