Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are bacteria-killing drugs that either inhibit the growth of bacterial cell walls (the protective wall surrounding the bacteria) or stop bacteria from replicating by manipulating bacterial DNA. Evidence of the use of antibiotics such as tetracycline
have been found in fossils dating back to 350 Common Era and has since evolved alongside human technology to become more effective and accessible to the everyday consumer. Common uses of antibiotics include disinfecting wounds, mediating safe child birth and curing food poisoning. Using antibiotics, countless lives have been saved in human history especially in major historical events such as World War II. The following link demonstrates the effects of the drug Penicillin on the outcome of World War II which was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928 (http://classroom.synonym.com/did-invention-penicillin-affect-world-war-ii-8709.html).
Bacteria vs. Antibiotic?
But, antibiotics are double-edged swords. Bacteria has been slowly adapting to various antibiotics and evolved so that some antibiotics are no longer effective. This is due to mainly two reasons:
- People have been misusing and overusing antibiotics for the last couple of decades which allowed bacteria to have an easier time adapting and building resistance to the antibiotics.
- Bacteria is a very flexible life from in the aspect that it adapts quickly and have quick mutation cycles.
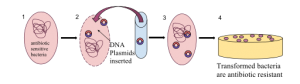
Dangerous cases have resulted where Super Bugs which are bacteria resistant to antibiotics have started to grow in hospitals infecting patients receiving various treatments. These cases have often resulted in mortality in these patients. The following illustration demonstrates the quick adaptability of a bacteria cell to an antibiotic.
The Battle is Won?
The information presented above must be shocking to some but rest assured because scientists believe that they have found an antibiotic that does not induce bacterial resistance. Teixobactin
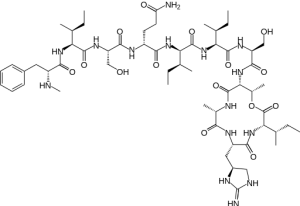
Teixobactin, Source: Wikimedia Commons
discovered earlier last year appears to successfully combat the development of bacterial resistance. The key in why this antibiotic is so effective in prohibiting bacterial resistance is the fact that it is able to inhibit bacterial growth in two methods as opposed to the normal one method attack of alternative antibiotics. Teixobactin prohibits the formation of both lipid II and lipid III in a bacteria which are detrimental in the formation of bacteria cells walls. Even if the bacteria is able to adapt by restoring the ability to produce of one of these lipids, the other lipid would still be inhibited.
The following is a YouTube video provided by Newsy Science which outlines the basics of what this new antibiotic can do and the mechanism behind it.
Hopefully, this new antibiotic marks the oncoming of a new age of drug use where antibiotic will no longer induce bacterial resistance.
By: Ming Lun (Allan) Zhu



![SEWAGE_SLUDGE_SETTLES_ON_BOTTOM_OF_BEAKER._SEWAGE_TREATMENT_PLANT_-_NARA_-_543811[1]](https://blogs.ubc.ca/sewagesludgeash/files/2016/01/SEWAGE_SLUDGE_SETTLES_ON_BOTTOM_OF_BEAKER._SEWAGE_TREATMENT_PLANT_-_NARA_-_5438111-150x150.jpg)