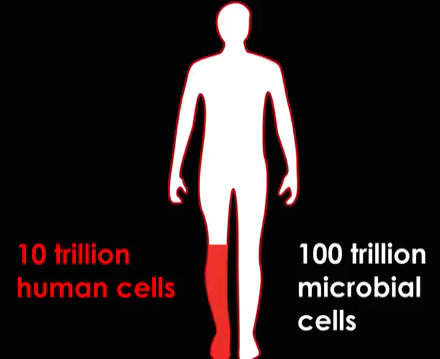
Have you ever wondered how many micro organisms are living inside us? Micro organisms are living organisms that cannot be seen with our naked eyes. They may be multicellular (made out of more than one cell) or unicellular (made out of one cell). Our human body is packed with trillions of microbes (or micro organisms). In fact, our own body cells are out numbered with a ratio of 1:10. So, we are technically 90% germs and 10% human. Microbes are found in all parts of our body in different proportions. Our lung has approximately 1000x less microbes than our mouth and has approximately 1 billion times less microbes than our intestines. Although most microbes are harmless to us, some may cause bacterial infections in humans.
Top three functions microbes in our body:
- Defense mechanism: Microbes in our lungs, intestines and our skin provide the first line of defense against harmful bacteria that enters our body. Good microbes found in these areas play an essential role in preventing the spread of harmful microbes by occupying space so less space are available for harmful microbes to settle down inside us. Thus, preventing us from bacterial infections that may cause fever, diarrhea or other problems. Other than that, researchers have found evidence that microbes that live inside us help promote our immune system cells to grow and replicate.
- Keeping us in shape: The trillions of microbe colonies in our intestines help digest fats and carbohydrates, facilitating the absorption of nutrients in cells. Our intestinal microbes also ferment food that we consume. The fermentation process produces chemicals that speeds up our metabolic processes. As a result, the microbes in our gut helps us keep in shape by increasing our metabolism.
- Detoxifies us: Microbes living in us are also capable of digesting toxins that we accidently ingest into less harmful substances. Therefore, preventing us from being poisoned. For example, the microbe Lacrobacillus probiotics found in food help the human body detoxify heavy toxic metals such as aluminum.
Where do we get microbes that live in our body? Most of our microbes that inhabit our intestines comes from the food we ingest. Our skin and lung microbes come from the air we are exposed to. Recently, researchers discovered that newborn infants get their microbes from their mother’s breast milk and vagina. Researchers found that the method of delivery may have an effect on the diversity of intestinal microbes in newborns. They discovered that infants born vaginally and infants born by caesarean section have different intestinal microbe composition. This indicates that we start to develop our microbe colonies from the day we were born.