Did you know that epilepsy is the fourth
most common neurological problem of our society?

Epileptic seizures are the result of abnormal activity in the brain. Source: Youtube
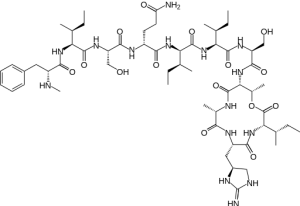
Epileptic seizures are the result of abnormal activity in the brain. Absence epilepsy is one form of epileptic seizures, characterized by a momentary loss of awareness, usually lasting less than ten seconds. What differs an epileptic seizure from a non-epileptic seizure is that it is recurrent and non-epileptic seizures may be induced by psychological issues or stress-related factors.

Absence epilepsy is often associated with children who have trouble in school, social problems, or who misbehave often. Source: Flickr
This condition is more common among children than in adults. As a result, absence seizures are often mistaken as daydreaming or periods of blanking out. Symptoms of absence seizures include fluttering eyelids, smacking of the lips, or rubbing fingers together. Absence epilepsy is often associated with children who have trouble in school, social problems, or who misbehave often. Most children will outgrow their seizures by age 18, however in some cases they can continue throughout the rest of their lives.
To understand a bit more about absence epilepsy, the podcast below depicts a scenario of a child experiencing absence seizures and how current research will fuel further medical studies to help with this disorder.

There are current studies being conducted on the causes of this condition at the University of British Columbia, and we interviewed Dr. Stuart Cain at the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health about his research on absence epilepsy.
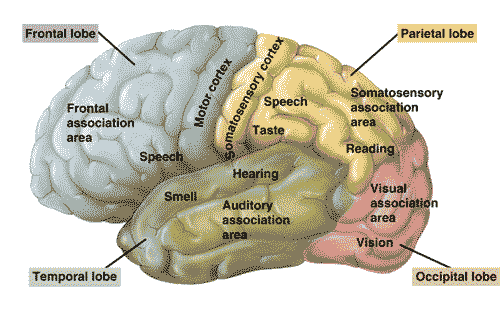
The main focus of Dr. Cain’s research is on calcium channels in the brain, and the role they play in absence epilepsy. It is found that the overactivity of certain calcium channels located specifically in the cells of the brain leads to a phenomenon known as “burst-firing”, and this is thought to be what triggers absence seizures.
The causes of absence epilepsy are still unknown, although there are many theories as to what causes an absence seizure. Dr. Cain believes that when overactive brain cells in one specific region communicates with two other regions of the brain and causes them to be stuck in a synchronous loop; this is what causes absence epilepsy.
The video below explains further on how absence seizures occur, and what the main findings of Dr. Cain’s research were:

There are currently two types of drugs available to treat absence epilepsy, and although they work for most people in stopping absence seizures from occurring, they have not been shown to be 100% effective.
Dr. Cain and his team of researchers’ study serve as foundation for further development of anti-seizure medications to control absence seizures. He believes that in order to find a drug that will be completely effective in controlling absence seizures, the drug will need to target the calcium channels in the brain which cause burst-firing. Dr. Cain suggests that the next move is to push pharmaceutical industries to create a drug capable of doing just that. If this proves to be successful, perhaps then children will not have to worry about absence epilepsy affecting their lives.
Posted on April 4, 2016
By Emma Peachey, Jenny Ung, Karanvir Gill, Harsh Bhatt