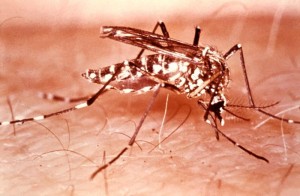
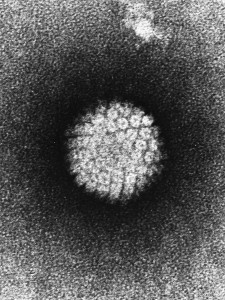
As many of us know, the dengue virus has affected billions of people since the early 19th century. The dengue virus is transmitted by mosquitos and is known to cause dengue fever. It is similar to other well-known viruses, such as the West Nile Virus, or the recent Zika Virus. Scientists were having difficulties creating a vaccine for the virus, as it appeared in four different serotypes (different strains). Creating a vaccine for a single strain could cause complications if the individual became infected with a different strain, as they would be unprotected. Also, if the vaccinated patient became infected with a different strain, they could go into dengue hemorrhagic shock, and die. Dengue hemorrhagic shock is characterized by bleeding, and severe low blood pressure. In most places where the disease is prevalent, all four strains of the virus cycle, thus it is important to create a vaccine that protected against all types of the virus.
The vaccine was tested in a small, double-blind trial with 41 volunteers. A double-blind trial is when neither the administrators of the vaccine nor the recipients know what they are receiving. Twenty of the recipients received a placebo (a fake shot, without the vaccine), and the remaining individuals were given the experimental vaccine. All participants in the trial were infected with a mild form of the virus six months later. The twenty individuals that were given a placebo showed symptoms of the virus, such as a rash, a low white-blood-cell count (cells of the immune system, that fight off viruses and infections), and other symptoms of the disease. The individuals given the experimental vaccine did not become sick, showed no symptoms of the virus, and did not have evidence of infection in their blood. The vaccine was developed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the results were posted in Science Translational Medicine. Beth Kirkpatrick, a participant in the trial and a professor of medicine at the University of Vermont, called the experimental vaccine “100 percent efficacious” in an interview.
The results were so promising that the NIH rushed the study to large-scale Phase 3 testing in Brazil, a country where the virus is prevalent. Phase 3 is the last phase of clinical trials, where the drug or vaccine is given to large groups of people to confirm its effectiveness and monitor side effects. They plan on enrolling 17,000 adults, children, and babies and finishing Phase 3 by 2018. These results also have important implications on a vaccine for the Zika virus. As Zika and dengue are similar viruses, scientists believe what they have learned from the dengue virus can be used to cut back the timeline for developing a Zika virus vaccine.
Kush Khanna