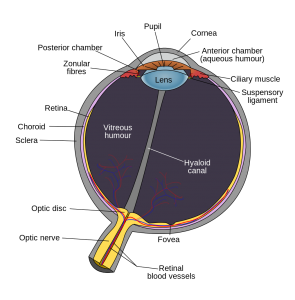
As the global population is aging, the number of elderly suffering from Alzheimer’s disease or dementia are predicted to increase to an estimated 75.6 million in 2030 and 135.5 million in 2050. Every 67 seconds, someone in the United States develops Alzheimer’s disease. Today, it is ranked the sixth leading cause of deaths in America. Although a growing number of researchers are studying the disease, Alzheimer’s disease is still the only cause of death in the top 10 that cannot be prevented, cured or slowed.

Alzheimer’s Disease Facts. Source: Alzheimer’s Association
A recently published study in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease showed that calories-burning activities are linked with greater gray matter volume in brain areas responsible for cognition and memory. Gray matter in the brain consists of most of the brain’s neurons responsible for muscle control, emotions, speech and memory. Patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease or dementia have decreasing gray matter volume in the brain, thus affecting their cognition and memory. Halting the reduction in gray matter volume might be the effective way in preventing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.

Normal brain vs. Alzheimer’s brain. Source: Bioinformatics
The study conducted by scientists at UCLA and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine revealed that participants who suffer from Alzheimer’s disease or dementia who are physically more active experience less reduction in gray matter volume than those who are physically inactive. Participants who are physically active also experience less cognitive and memory declines.
Researchers gathered five years of data from 876 participants aged 65 and older. Brain scans, cognitive tests and interviews were conducted to gather accurate data about their cognitive health, physical health and physical activities over the period of five years. Participants filled questionnaires to evaluate their leisure time, physical activities and cognitive abilities.
Scientists revealed that those who exercise the most have a 5% larger gray matter volume than those who exercise the least. 5% decrease in gray matter volume corresponds to 50% lost in cognitive and memory functions. The brain scans revealed that participants who exercised the most have denser gray matter in the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes, which are the areas responsible for learning, cognitive tasks and memory.
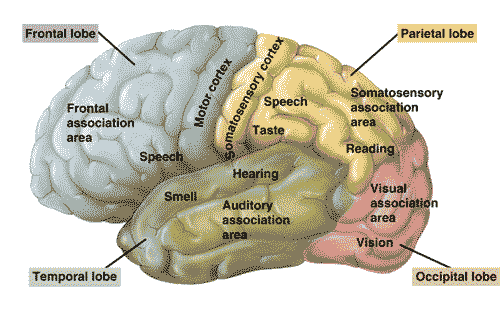
Frontal, parietal and temporal lobes of the brain and their functions. Source: My Brain Tests
Scientists are encouraging doctors to start dementia and Alzheimer’s disease prevention by encouraging regular physical exercise instead of waiting for memory loss to start. Past studies have shown that delaying the development of Alzheimer’s disease by ten years would eliminate the disease as the elderly would die of other causes first before developing the disease.
Even though scientists have no fixed number of how much exercise it takes to prevent dementia, researchers estimated that the people need about an extra 500 calories per day to be burnt. Luckily, it doesn’t matter how the extra calories are burnt, as long as they are burnt.