Imagine a world where you are able to gain access of your entire genome within minutes. Not only will you become aware of what makes you unique, but it will also help with the diagnoses and treatments of many diseases. Thanks to next-generation sequencing technologies like Illumina and 454, we are one step closer to converting this fantasy into a reality.
Currently, these new technologies have the ability to sequence five human genomes in one week. This is astonishing because each genome is around 4.3 meters long with over 20,000 genes that code for proteins. Given its efficiency with deciphering human DNA, you would expect high performance on bacterial and archaeal microorganisms that have smaller genomes. By determining their genetic information, it is possible to compare different types of DNA and look back on the evolutionary origin of these life forms.
Check out this podcast to learn more about the evolutionary background of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya:
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
A study done by Dr. Nislow and his colleagues has demonstrated the usage of next-generation sequencing, particularly Illumina. They compared the structure and function of chromatin, a DNA- protein complex which contains genetic information, in Archaea and Eukarya by sequencing their genomes. The video below gives a more detailed overview of the research:
 Youtube user: stephanieem (SCIE 300 Group 1)
Youtube user: stephanieem (SCIE 300 Group 1)
In addition to their rapid sequencing speed, these new technologies have other advantages over the conventional methods. Not only are they highly accurate, but they also provide a larger amount of data for a lower price. For example, when using Illumina, it costs around ten cents to sequence a million nucleotide bases, the fundamental units of DNA. Although this may seem a whole lot, each human cell has over 12 billion bases of DNA!
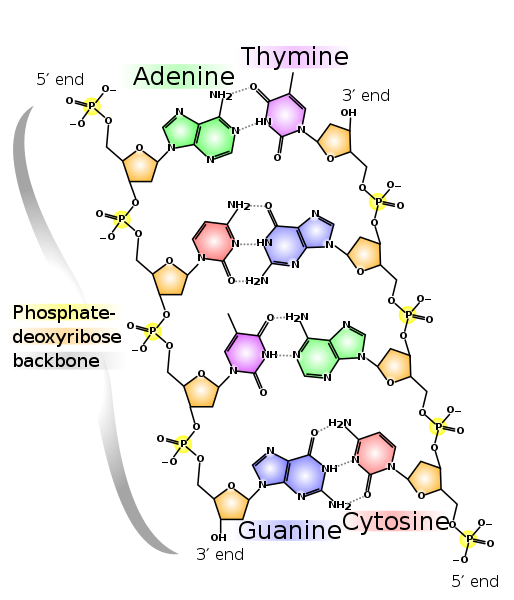
Picture of DNA showing the 4 different nucleotide bases. Author: Madprime via Wikimedia Commons
With the advent of the next-generation sequencing technologies, it is now possible to achieve many tasks that would otherwise remain unresolved. As they continue to become more advanced, many excitements in this field lie ahead. You never know, genome sequencing might even become an application on our computers where we will be able to see for ourselves what makes each one of us so unique.
-Group 1: Daniel (Sanggi) Hong, Stephanie Mrakovich, Maral Altanbadralt, Jing Xiang Yang

