Cancer is a mysterious silent killer whose cure, even to this day, cannot be found. Many studies have found a link between weight gain and obesity to increased risk of cancer. Could the solution to cancer prevention be something as simple as getting enough exercise and having a proper diet? As many of you know, the idea of following a healthy diet and exercising regularly is beneficial and we are constantly reminded by our friends, family and even the media. However, unknown to many of us, what we think is a common idea may be very effective in preventing obesity-related cancers.
How exactly does being overweight relate to increased cancer risks you ask? Simply put, it has been hypothesized that many hormones or proteins involved in the development and progression of diseases such as cancer, are secreted by adipose tissue. Therefore, the more fat accumulated in the body, the more hormones secreted or “genes” expressed that can take part in the pathways leading to cancer. To examine the effects of weight loss on fat tissue gene expression and subsequently, the amount of hormones secreted, Dr. Kristin Campbell, a researcher at the University of British Columbia, and associates studied the effects of exercise and diet on body fat tissue.

Dr. Kristin Campbell working with Scenery Slater, a cancer patient by Martin Dee via http://www.publicaffairs.ubc.ca/2012/06/06/blame-it-on-chemo-brain/
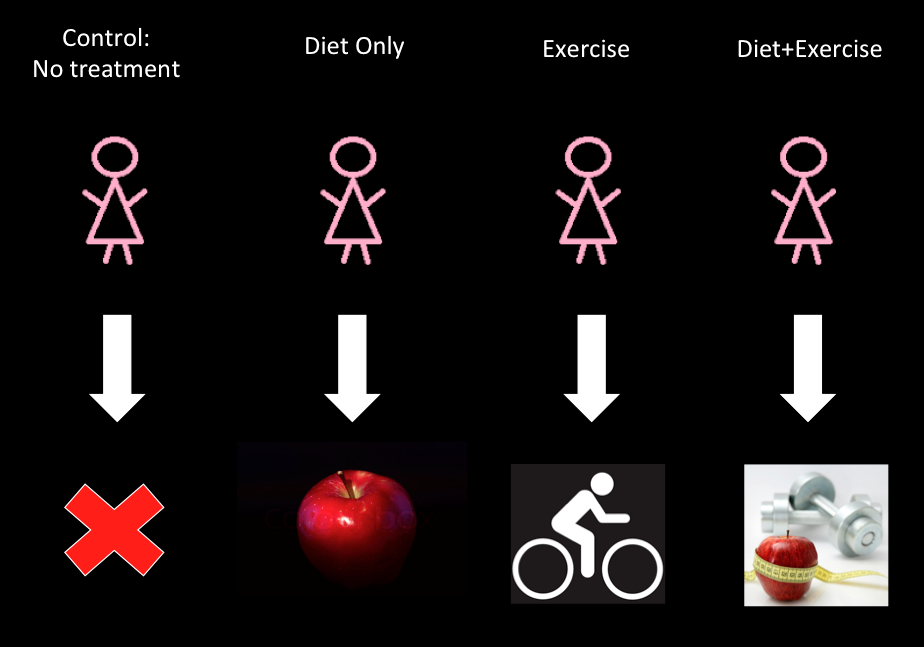
Forty-five postmenopausal women participated and were divided into 4 treatment groups: a control group (no treatment), a calorie-restricted diet group, an exercise group and a diet+exercise group. Blood and adipose tissue samples were taken from every participant before and after following the treatments for 6 months. The samples were then analyzed for changes in hormone levels or fat tissue expression in the body. It was found that women who followed only a calorie-restrictive diet lost the most weight and greater weight loss was correlated with greater changes in fat tissue gene expression. In other words, reducing the amount of body fat ultimately reduces the chances of developing diseases such as cancer.
For further details on the motivation of Dr. Campbell as well as the findings of the research, take a look at the video below:
Youtube via whywontmynamefit
Although the subjects were all postmenopausal women, Dr. Kristin Campbell notes that weight loss can also reduce the risk of colon cancers and other obesity related diseases that affect men and women equally. From the research findings, we can see how important being healthy is for not only older generations, but for the younger generations as well. We hope our blog motivates others to live a healthier lifestyle.
With that being said, listen to the podcast below for Dr. Campbell’s suggestions for exercise and diet regimes:
Audio clip: Adobe Flash Player (version 9 or above) is required to play this audio clip. Download the latest version here. You also need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser.
– Grace Lam, Alice Lin, Ashkan Nasr, Derek Rejto