The popularity of fitness training seems to have increased exponentially over the past couple of years or so. Fortunately, this means that people generally are more educated about how to train and eat properly. However, although people are finally realizing that the “less is best” diet is the most effective, many individuals who are mindful of caloric intake and expenditure do not know that there is an association between the level of this energy balance and body composition. Enter John Berardi‘s principle of G-flux.

Balance of energy in the body (Found at: http://www.180degreefitnesssystems.com/images/negative_energy_balance.jpg)
John Berardi argues that a higher energy balance, that is, a higher amount of energy into the body accompanied by higher energy expenditure by the body, is superior for body composition. So how does G-flux work? Take, for example, an individual who does little to no physical activity from week to week. This person’s daily requirement of calories to maintain their current body composition will be low, due to low energy expenditure. If the same individual were to engage in five to seven hours of weekly physical activity, their energy expenditure will be much higher. Provided that the energy taken into the body (food eaten) balances the caloric expenditure, energy balance level or G-flux, will be higher. G-flux says that the net effect of this higher energy balance is a body that not only possesses a superior composition, but performs better, also.
Ultimate couch potatoes. Author: LAIntern, via Wikimedia Commons
VS

Usain Bolt after World Record breaking 100m at Beijing Olympics. Author: Richard Giles, via Wikimedia Commons
Some might ask how the body can produce a better composition while still taking in maintenance levels of calories. Many experienced athletes, fitness buffs and studies will tell you that in order to cut fat, a caloric deficit must be achieved – the amount of calories taken into the body (through food) is less than the calories burned through exercise and other activities. This is a tried and true method for leaning out the body, but in a state of caloric deficit the body builds little to no muscle, and other effects such as fatigue may occur. In a state of high G-flux, however, the body is in an environment where fat loss is promoted through intense and frequent activity while still being able to build muscle at maintenance calories.
A great (and humorous) explanation of G-flux by YouTuber, Omar Isuf.
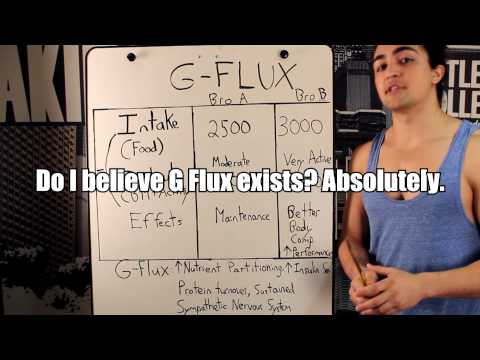
How can you increase your G-flux? Simply increase your weekly exercise. Choose physical activities that are relevant to your fitness goals and do them for a minimum of five to seven hours a week, while increasing your food intake accordingly to achieve that higher energy balance.
– Curtis M.
For more information on diet and caloric intake, see Earvin Remandaban’s post.
