*WARNING, GRAPHIC IMAGERY INCLUDED BELOW*
Ink printers are used daily to print assignments and papers. The general population is also relatively aware of 3D printers, printers that print three dimensional objects of any shape. Now, a new kind of printer is being developed to print human tissue.Researchers at Wake Forest University, lead by Anthony Atala, have been researching the treatment of burns.
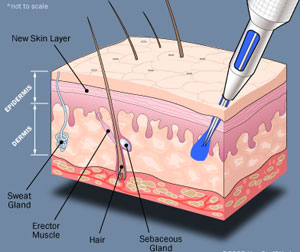
Current methods to treat burns include skin grafting. Skin grafting requires doctors to take skin from a healthy donor site on a person’s body (an area that is usually covered by clothing) and transplant it to the damaged site. The new skin graft is held in place by stitches and dressing. Unfortunately, this procedure is prone to infection and requires the damage to the donor site to help the damaged site. Another method requires skin cells to be grown in vitro then, applied to the affected area on the body. This method requires careful handling, as the skin grown in vitro can break down or warp in shape very easily.
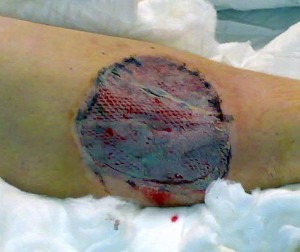
Skin graft.
Image credit: Wikipedia
This new technology to print human tissue is a medical breakthrough. Using the same technology as a regular inkjet printer, researchers were able to successfully print skin tissue. Instead of the inkjet printhead being connected to a well of different colours of ink, the printhead is connected to “wells” of different types of cells. A laser first scans the burn area and the printer can print skin cells directly onto the wound, thus eliminating the complications that arise from the traditional methods of burn treatment.
The research team is also looking to successfully print organs. Unlike skin cells which could be printed flat, organs would need a 3D mould for the printer to print onto. They have successfully printed bone and mouse hearts and implanted them into mice. The one drawback is that organs do not exist as an island. They require connections (blood vessels, nerves, etc) to other parts of the body. While the tissue printer can print the organ, there is further work that needs to be done to figure out how to print the organ’s connections. Skin on the other hand, is more simple. Once the printed skin is applied to the body, it absorbs the body’s plasma and blood vessels begin to connect to it.
Since this development occurred a while ago (year 2010), more recent developments by another research team at Cornell have been able to print human heart valves. Other human body parts have also been successfully printed. These are important developments in the area of organ and tissue transplants. Here is a video illustrating tissue printing:

– Jade Lu











![By Jorge Barrios (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://blogs.ubc.ca/communicatingscience2014w112/files/2014/10/256px-Glass_of_Water-230x300.jpg)