Dyslexia is also commonly known as a life-long language based disability, where individuals have difficulties with processing language. Problems may include challenges in spelling, reading quickly, and pronouncing words when reading aloud. Dyslectics may also hear things that are not apparent to others, and have difficulty putting thoughts into words.
Below is an image of what letters may look like to a dyslectic. As you can imagine, words may easily get jumbled up, and thus look incoherent.
Studies show that individuals with dyslexia have difficulty understanding phonemes, which are the smallest unit of speech. Despite this, people diagnosed with this neurological condition have normal intelligence, along with a normal desire to learn. Take Albert Einstein for example, who was dyslectic but had an IQ of 160.
Dyslexia is usually recognized during the early stages of life, especially in school, and is not only one of the most common learning disabilities, but also one of the least known. It is also often associated with ADHD, where these two disorders have been found to have the same genetic background.
Not everyone who has this condition experiences it in a similar way. Most have mild symptoms, only having problems with reading and writing, for instance. However mild though, this is a frustrating situation for many dyslectics, especially in communicating their knowledge.
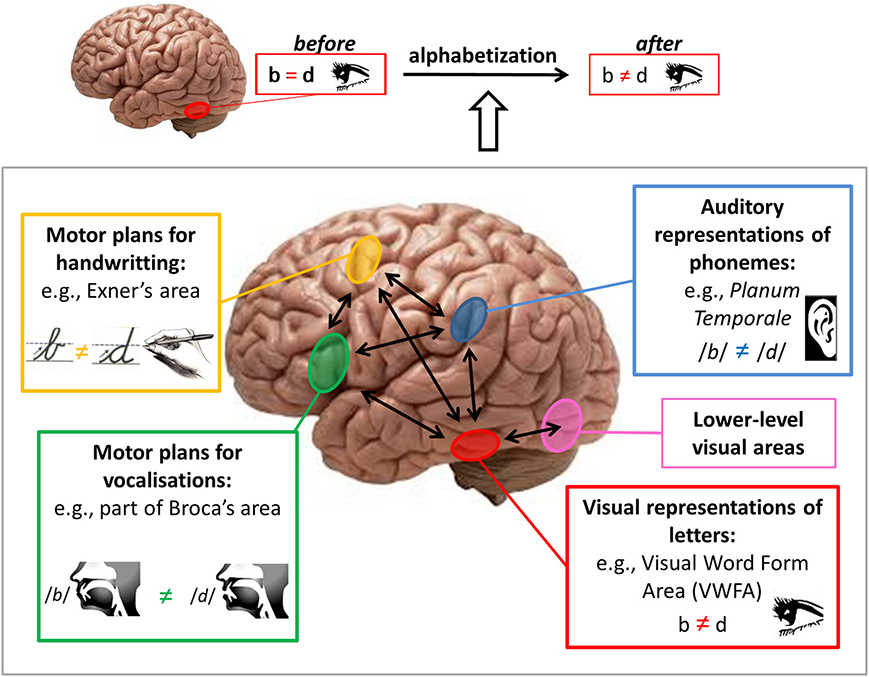
Dyslexia is widely accepted as genetic in origin, meaning individuals inherit this disability from a parent. A study has found that individuals with a deletion of the DCDC2 gene had trouble detecting visual movement. Experts have also found a link between a mutation in the ROBO1 gene and dyslexia. In other words, dyslexia results from structural differences in the brain, particularly in the left hemisphere. Therefore, a dyslectic person uses his right hemisphere instead of his left to read, which can cause problems as the left hemisphere is programmed for processing language while the right is not. The image below demonstrates brain pathways in the brain that could potentially have lower activity levels or weaker connections in a person with dyslexia.
There is no current cure for this disability but treatments are available to help them manage their symptoms. Therapy most often includes educational tools to enhance the individual’s abilities. Many dyslectics have successful lives, take Alexander Graham Bell, John Lennon, and Henry Ford for example, who were all dyslectic, but achieved great things throughout their time here on earth.
The video below by DNews clearly summarizes this disorder, stating some its possible causes and the importance of understanding dyslexia.
To conclude, it is important for us to understand how the brain of dyslectics work so that we may identify potential symptoms and help those affected deal with the challenges they struggle with in an effective way.
-Daniela Castillo