While most people are familiar with the risks that Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) pose, sadly a shockingly large knowledge gap and a false sense of security remains for many. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a particularly worrying example due to the fact that it is estimated to be the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States. Unlike most other STIs, HPV can be transmitted via skin-to-skin contact with the infected site. As a result, most people are unaware that the use of a condom does not guarantee protection against HPV. Furthermore, the complete breadth of effects are still being understood. Considering there are over 170 different types of HPV that have varying effects on each gender, questions of treatment, diagnosis, and tracking of the virus become quite complex.
It is estimated that all sexually active people will be infected by HPV at some point in their life. The vast majority of these cases (70-90%) are cleared by the body within about a year; however, this does not mean the virus is harmless. Some infections may persist and most commonly exhibit themselves as genital warts, or in certain cases may eventually lead to cancer.
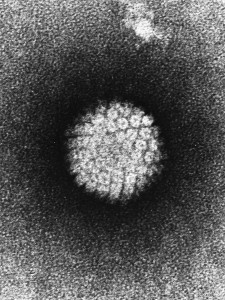
TEM of HPV. Source: Wikipedia Commons
Certain types of HPV, the most common of these being HPV-16 and HPV-18, and their link to cervical cancer were identified quite early on after the virus was first identified. Together these types have been found to account for over 99.7% of cases of invasive cervical cancer in women. Fortunately, a relatively straightforward test known as Pap smear can be used to test for abnormal cell growth and precancerous conditions. It is now recommended that women over the age of 21 should have a Pap test done at least once every three years. The use of three different vaccines has now become the focus of HPV prevention. These vaccines have proven to be extremely effective at preventing the most common forms of cancer caused by these viruses. A combined vaccine is now provided for free to all girls in Grade 6; however, those born in 1994 or earlier should contact their health care provider to get the vaccination.
The HPV vaccination is also recommended for all men aged 9 to 26, although it currently is not provided for free for most men in B.C. It is now understood that HPV increases instances of certain cancers of the penis, anus, or oropharynx. More recently, it was determined that oral HPV infection increases the risk for both head and neck cancers. Although, since the recommendation for vaccinations has only been made relatively recently by the Public Health Agency of Canada, the vast majority of adult men remain unvaccinated. A further complication is that there is currently no approved way to test for HPV in men so prevention and information remain the only solution.
However, promising research published in JAMA Oncology and successful phase 1 trials in Europe show that doctors and researchers are beginning to get a handle on this very serious virus.
The YouTube video below is a great summary of the potential health risks of HPV.
Credit: Nucleus Medical Media on Youtube
– Gulaab Sara




![SEWAGE_SLUDGE_SETTLES_ON_BOTTOM_OF_BEAKER._SEWAGE_TREATMENT_PLANT_-_NARA_-_543811[1]](https://blogs.ubc.ca/sewagesludgeash/files/2016/01/SEWAGE_SLUDGE_SETTLES_ON_BOTTOM_OF_BEAKER._SEWAGE_TREATMENT_PLANT_-_NARA_-_5438111-150x150.jpg)