People who have rare metabolic diseases, such as Maple syrup urine disease depend highly on donor transplantation. But is there an alternative treatment if donors are low? Not to mention the high expenses of a transplant?
But… you might be wondering… what exactly is maple syrup urine disease and where does it get its name?
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare disease because it follows an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance, one of the ways a disease can be passed down through families. This means patients inherit MSUD if both their parents have an abnormal gene. MSUD causes a defect in the way our body breaks down the three essential amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
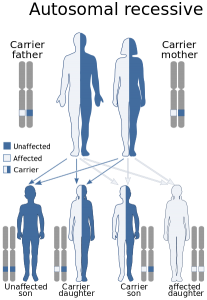
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) follows a autosomal recessive mode of inheritance. Source: Wikipedia Commons
It is characterized by the distinctive maple-syrup scent found early on in urine samples of infants. They are important because essential amino acids cannot be made from the body, so they must come directly from our diet. The defect causes these three amino acids and their by-products to build up in the body. As a result, MSUD patients need precisely monitored diets (measured to the very milligram!) to avoid consumption of these amino acids, while still obtaining the other essential amino acids the body needs.
If MSUD conditions are left untreated, they can lead to coma, seizures and even death before reaching three months in age.
Liver transplantation is shown to be effective in treating MSUD because the liver is composed of an abundance of enzymes which appear to normalize amino acid levels, sometimes even allowing patients to fully adopt their normal diets again.
So organ transplantation is usually the solution to metabolic diseases but because of the high demand, is there a more accessible alternative?
Noting the high activity of fat tissue relative to muscle tissue in the body, researchers from Penn State College of Medicine tested the effect of body fat transplantation with genetically engineered mice with MSUD. They transplanted two grams of fat into the mices’ back or abdomen and found that when they implanted fat into the mices’ back, the amino acid levels dropped greatly in the transplanted MSUD mice compared to non-transplanted MSUD mice.
Transplanting fat into the abdomen of the mice did more harm than good and caused inflammation in the process. The results of this study were recently published in the journal Molecular Genetics and Metabolism.
Their study concluded that the amount of fat injected had no effect on the results. So this must mean that there will be further experimentation with fat transplantation. Fat transplant can be an alternative to liver transplant because it may be a more efficient approach as it is relatively inexpensive and it may be easier to find donors.
Wayne and Chad’s personal account on their child living with MSUD: 
Posted on January 25, 2016 By Jenny U