Thank you to each of my students who took the time to complete a student evaluation of teaching this year. I value hearing from each of you, and every year your feedback helps me to become a better teacher. As I explained here, I’m writing reflections on the qualitative and quantitative feedback I received from each of my courses.
After teaching students intro psych as a 6-credit full-year course for the past three years, in 2013/2014 I was required to transform it into 101 and 102. Broadly speaking, the Term1/Term2 division from the 6-credit course stays the same, but turning Term 2 of Psyc 100 into a semi-standalone Psyc 102 proved more challenging than converting Term 1 into 101. Because these two courses really still form one unit in my mind, and I structure the courses extremely similarly, I will discuss them in tandem.
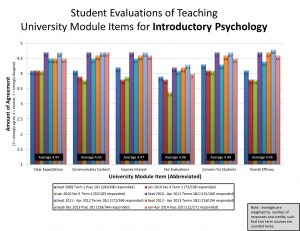
Across both courses, quantitative feedback was similar (albeit a bit higher in 101 than 102). Students rated the textbook equally high (4.2 & 4.3/5), which makes sense because I use the same text for both, and many students have told me informally that they enjoy reading the book (some qualify this endorsement with “for a textbook”). Check out my overall UMI scores from this year and all previous years here (click to enlarge, and click here for further discussion of UMIs):
In the qualitative feedback, many of the same positive and helpful features were highlighted by students in both courses. Overall, students report enjoying and finding valuable the clickers, classroom discussions (often tied to clicker questions), films, opportunities to apply what is being learned, the 3-midterm format that helps stay on top of things even if it’s slightly annoying to be so frequently tested, music before class, the organization of class periods, my enthusiasm and energy, my effort to learn many students’ names, and the Invitational Office Hours. Capturing many of these commonly-mentioned features, one student from Psyc 102 wrote,
“It was incredibly impressive how she tried to learn the name of every single student that she interacted with, despite the size of the class. The IOH were also a surprisingly fun experience. The class was very interactive, which definitely helped me learn, and even though I was unhappy about having three midterms at first I think I have to conclude it made studying for each one much easier and less stressful.”
One new element I added to both courses this year were five mini-papers which I called “Writing to Learn” (W2L) assignments (replacing a single 500 word paper I used to assign to be marked by TAs; see last year’s reflection for rationale). Students picked a topic from each of the two chapters about to be tested, wrote a paragraph explaining and applying the concept to their lives, then read 5 peers’ papers and gave feedback to them using peerScholar software. Students received feedback from their peers, and were able to choose any two topics to improve and reproduce on the final exam (no notes!). Overall, students reported finding the Writing to Learn assignments helpful for learning, and some mentioned that reading others’ work was helpful as well (both of these results are consistent with past research on similar writing assignments and peer review). My TAs have reported being able to grasp whether students knew what they were talking about from the writing section on the exams – and my test scores were higher than in previous years, so the goal of increasing learning seems to have been met! However, of the students who mentioned the W2L assignments, many noted that quality of peer feedback received was low. Dr. Peter Graf and I are just starting a project to deal with this very issue of enhancing peer feedback. It may take a couple of years to figure it out in a way that’s scalable to 300-400 students at a time, but we’re working on it.
Interestingly, a couple of students in each course noted my responses to student incivility. In one case it was failing to follow instructions to complete the bubbles during the exam time given, and another case (mentioned a few times in 102, actually), was my response to students talking in class. Side chatter is really only a problem in my first year courses – and it’s a consistent one that varies in severity year-to-year with different cohorts. Interestingly, Gillian Sandstrom and I have a paper about to come out in Teaching of Psychology showing that some chatter is a good thing: it can build a sense of community in a large class. But it can feel disrespectful and distracting to me. Perhaps I should consider building in even more opportunities for structured conversation, because clearly it’s going to happen anyway.
In 102 this year, rather than devoting a whole week to Chapter 2 Research Methods – which I do in 101 in the same place I did back when I taught the 6-credit version – I decided to split it up and cover topics as they came up throughout the term. For example, I used intelligence testing as a chance to discuss measurement and survey designs, and social psychology (specifically Milgram’s studies) as a chance to address the ethics of deception in research designs. Although I think this was a solid solution in theory, in practice there were definitely times when I felt like I was awkwardly wedging topics in to 102. Indeed, a few students mentioned this flow problem too – and it seems to be students who took both 101 and 102 with me who noticed the difference. Hopefully next year I’ll be able to smooth topics out a bit more effectively, perhaps cutting even more material to make more room for these new topics and ensuing discussions.
Although I still would prefer to teach intro psych as a unified whole with the same students over the whole year, apparently that’s not an option any longer. I have begun the process of converting this course into two halves effectively, and given the feedback above, I think I’m heading in that direction.

 Follow
Follow