Endorphin is closely related to morphine, and morphine is a drug that effectively removes pain after getting hurt or surgery, and also gives thrill to people as if they fly in the sky. Because of this, morphine freed countless people who have suffered from pain, but also played a huge role in destroying people by making them addicted.
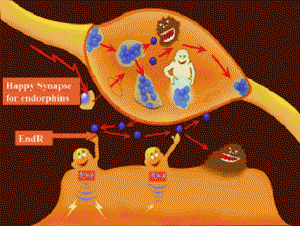
So, in 1970s, many researchers studied about this. And later, they discovered that there is a substance that performs a similar role like morphine in our brains. And it is about 100 times stronger than morphine. Thus, by definition, the substance is endogenous morphine, which means that it exists inside a brain. To call it short, it is called as endorphin.
This substance is secreted when people get stress to counteract it. Endorphin is a very thankful substance that relieves anxiety and pain to make people happy. When people get stress from climbing high mountains and skydiving, the brains secret endorphin to make them feel less pain and thus feel as if they fly the sky.
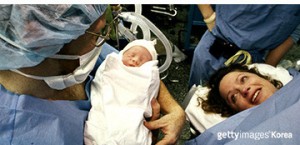
Also, an interesting fact is that the secretion of endorphin increases when people feel stress, but is restrained when they are happy. For example, when women are about to give birth, the level of endorphin reaches the maximum point in both mothers’ and babies’ brains to deal with the situation. After giving birth, the level of it decreases rapidly.
Therefore, it seems that babies are exposed to drugs from the moment when they are born. And there is always possibility that anyone can get addicted. So we need to be very careful not to become addicted to drugs.

This shows how endorphin works for people’s body by William Bloom. (This video is from the youtube username William Bloom.)
-Jong Jin Park