Researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and the University of Glasgow in Scotland conducted a study that showed larger, taller animals, including humans might live shorter lives, relative to their smaller, shorter counterparts because of the changes in DNA which are associated with faster growth and aging.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Source: Wikipedia Commons
In the theory of natural selection, it was well understood that animals who were larger in size had a competitive advantage in terms of strength and in feeding over those who were smaller in size. As a result, biologists tried to make sense of why animals did not continue to grow after a certain point. Previous studies revealed that although larger animals do, on average, live longer than smaller animals, for example a whale has on average, a longer lifespan than a penguin and a cat, the link between body size and longevity can only be observed within species.
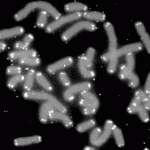
Human chromosomes (grey) capped with telomeres (white). Source: Wikipedia Commons
What changes in DNA are associated with biological aging?
Like the plastic tips at the ends of our shoelaces, telomeres cap each strand of our DNA that protect our chromosomes and therefore prevent our cells from aging and dying. The length of our telomeres represent our biological age because they continue to shorten as the cells in our body continue to divide.
In determining optimal body size, the researchers focussed their study on the relationship between body size and telomere dynamics. In the remote Leka island in Norway, they worked on a population of wild house sparrows and collected data on the sizes of their telomeres. Larger sparrows with larger bone structures have shorter telomeres and were observed to live shorter lives, relative to their smaller counterparts.
Scientists have concluded that there is association between shorter lifespan and telomere length. Shorter individuals are likely to have longer telomeres, which has an advantage against biological aging and overall risk of disease.
Professor Pat Monaghan, Regius Chair of Zoology at the University of Glasgow, who supervised the telomere analysis stated that “Growing a bigger body means that cells have to divide more. As a result, telomeres become eroded faster and cells and tissues function less well as a result.” This explains why larger, taller individuals tend to have shorter telomeres because they undergo more cell divisions than smaller, shorter individuals. Monaghan also noted that “The reason why the bigger individuals have shorter telomeres might also be related to increased DNA damage due to growing faster. Being big can have advantages, of course, but this study shows that it can also have costs.”
The results of their study were recently published in Proceedings of the Royal Society Biological Sciences.
Posted on March 14, 2016 By Jenny U