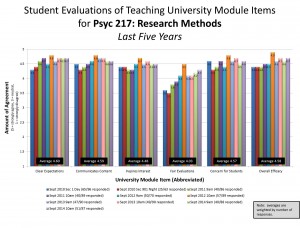
Thank you to each of my students who took the time to complete a student evaluation of teaching. I value hearing from each of you, and every year your feedback helps me to become a better teacher. Each year, I write reflections on the qualitative and quantitative feedback I received from each of my courses, and post them on this blog. I have graphed the quantitative student evaluations here. Note that I was on sabbatical for the 2016/2017 academic year, so I’m writing these posts in response to 2015/2016 student feedback in preparation for Fall 2017.
A recap on this course: After teaching students intro psych as a 6-credit full-year course for three years, in 2013/2014 I was required to transform it into 101 and 102. Broadly speaking, the Term1/Term2 division from the 6-credit course stays the same, but there are some key changes because students can take these courses in either order from any professor (who uses any textbook). These two courses really still form one unit in my mind so I structure the courses extremely similarly.
Across PSYC 101 and PSYC 102, the two halves of Introductory Psychology, are pretty consistent in how I teach them and the reception they get from students. In both cases, I think the things I need to keep strong are enthusiasm and care for students as humans, as well as a variety of activities during classes, including engaging students with each other, but also lecture, videos, demos. My area for growth is around assessments (i.e., the least fun part of teaching, but an essential part of learning!). Two-stage exams are here to stay – they make test day fun, offer students feedback, and help them learn. After all these years I still haven’t quite managed to find the right balance between textbook-only and class-only material (and do I unassign portions of the text that won’t be tested?). And students have long been calling for representative practice questions. Fingers crossed that MyPsychLab can help with that. [Follow-up: As I suspected, questions in MyPsychLab are not challenging enough. Erg.] Regarding the written assignments with peer assessments, I got a mixed bag of feedback that really only point me at something’s not quite right for some students. I wonder if I need to devote more class time to the exercise (e.g., show examples of papers, feedback, including the grade range to be expected by peers)? Not sure. Time to consult the experts! If you’re interested in a distilled version of student comments, all summarized in a table that sort of compares 101 and 102, interjects some of my thoughts and recommendations for students, here you go…

 Follow
Follow