Function and Purpose of the Nervous System:
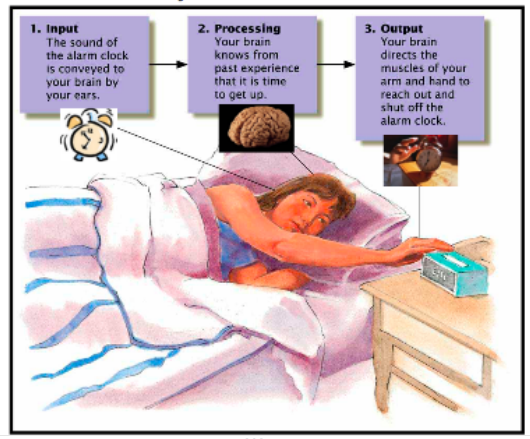
The nervous systems role is to take input (usually in the form of sensory information from sensory neurons), process that information and determine the course of action, and then to follow through with that action (usually through motor neurons) in regards to that stimulus.
Even though our nervous system is incredible developed and complex, all living things respond to stimuli. This means they take input, process it, and provide a response (output). This is the purpose and function of the nervous system!
Divisions and Roles of the Human Nervous System:
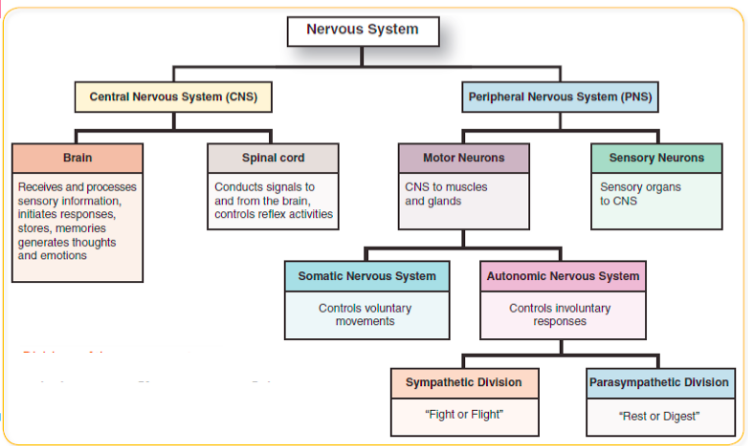
The Central Nervous System: The Brain:
The Basics:
- Stores and Processes sensory information
- Generates thoughts and emotions
- Site of “consciousness”
- Along with the spinal cord, the brain coordinates and regulates everything in the body!
Structure:
- Surrounded by three protective membranes called “meninges”
- Liquid found between the middle and inner layer is called cerebrospinal fluid.
- This fluid acts as a shock absorber and helps carry nutrients to cells of the brain.
- Divided into two halves by a central fissure – creating a left and right hemisphere!
Myth:
- People who are left brained are scientific, logical, and analytical.
- People who are right brained are creative, artistic, and emotional.
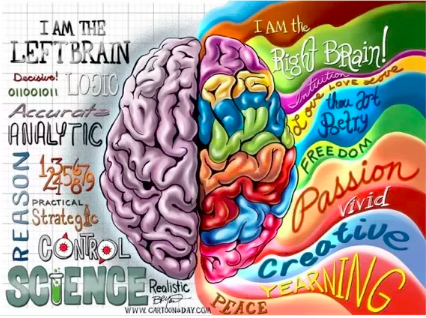
Truth:
- There are processing differences:
- Speech production/comprehension = left hand side
- Face recognition/sense perception = right.
- Most tasks do not fit neatly – require both sides of the brain for each task!
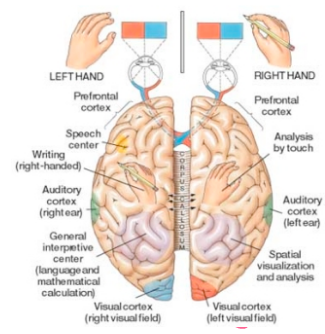
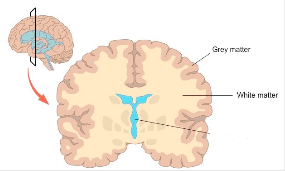
- Contains both grey matter and white matter.
- Grey Matter – Composed of cell bodies and unmyelinated neurons.
- White Matter – Composed mostly of long range myelinated neural axons (think like the wires of a telephone)
Parts of the Brain:
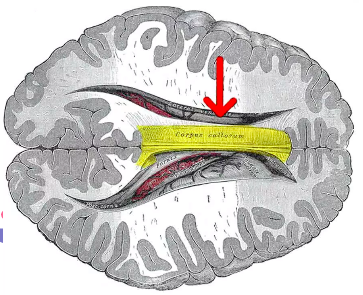
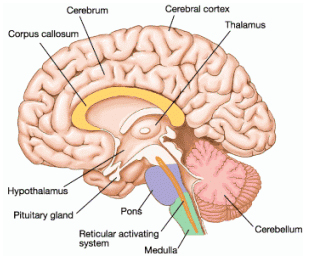
- Corpus Callosum – Bridge between right and left hemispheres of the brain
- Hypothalamus – Helps maintain homeostasis. Regulates hunger, thirst, sleep, body temperature.
- Makes hormones and controls the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary Gland – holds and releases hormones
- Thalamus – Receives sensory information from the spinal cord and relays it to the correct region of the cerebrum.
- Called the “sorting centre” of the brain.
- Sorts things that need immediate attention (and can ignore less important things i.e. Mr. Pletsch…
- Medulla Oblongata – Controls heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, and other unconscious reflexes.
- Cerebellum – Ensures smooth movements and coordinates complex movements and balance.
- Cerebrum – The central processing area of the brain.
- Involved in conscious thought.
- Where non-reflexive associations are made.
- Large and complex – divided into many lobes which have their own specializations.
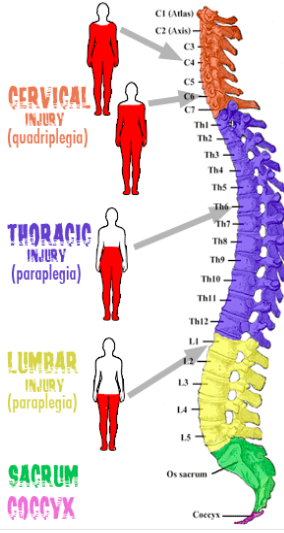
The Spinal Cord:
- Runs from the brain down the back through the protective, bone vertebrae.
- Transmits motor output to/from the brain/sensory receptors. Centre for reflex arcs
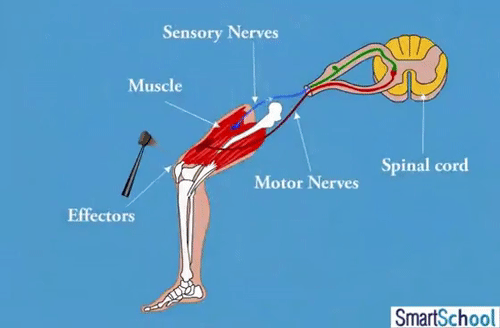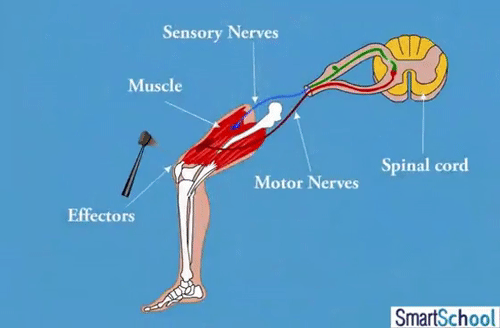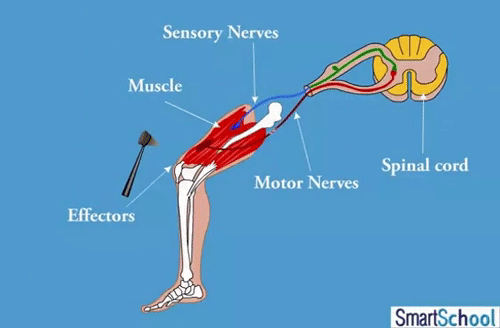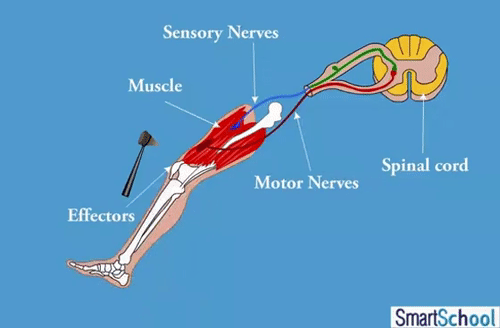
- Connects are peripheral nerves from around the body to the CNS.
- These nerves branch out between most vertebrae.
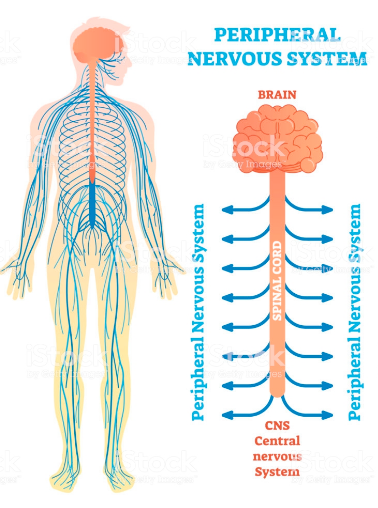
Divided into four major regions:
- Cervical region – Corresponds to the neck region
- Thoracic region – Corresponds to the thoracic (chest cavity)
- Lumbar region – Corresponds to abdomen and lower back
- Sacral region – Tailbone area
Comments by shaun pletsch