Cities are slowly transitioning from the familiar yellow High Pressure Sodium (HPS) lamps to cooler-hued LED lights to reduce operational costs. LED lamps provide better visibility, consume 70% less energy, and also have a lifespan five times longer than HPS lamps. These new street lamps are more environmentally and financially friendly, but how are they affecting our health?
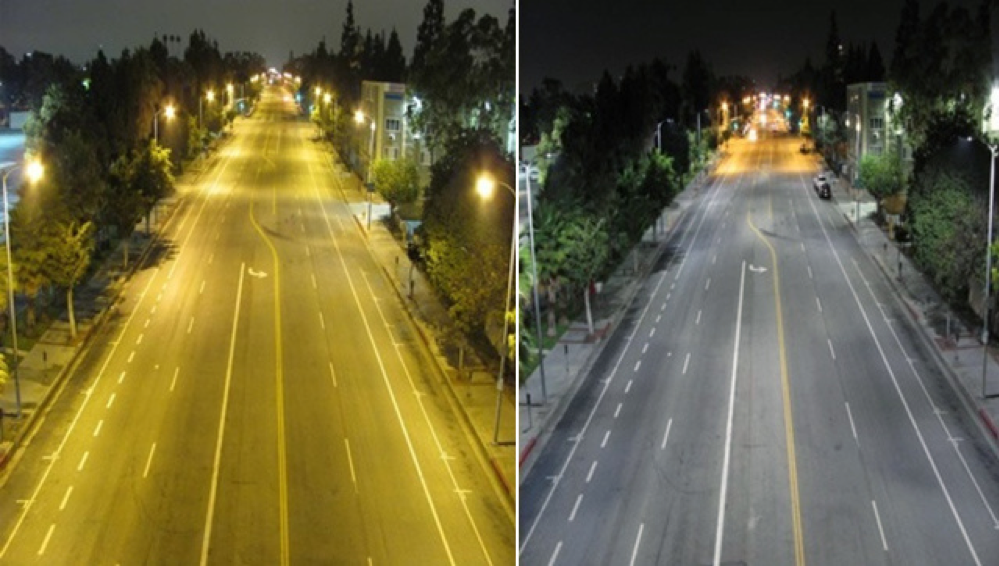

Los Angeles’ Hoover Street before (HPS lighting) and after (LED lighting). (Credit: LA Bureau of Street Lighting via CNN)
Sleepless nights
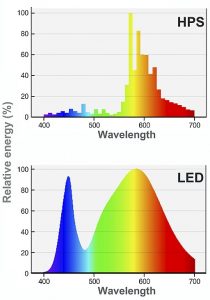
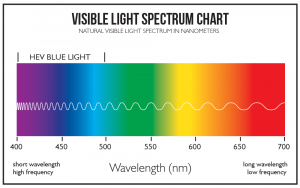
Contrasting HPS, LED emit light at blue wavelengths and negatively affects melatonin secretion and thus sleep quality and quantity. (Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Compared to HPS lamps, LED lamps have five times greater impact on circadian rhythms, the sleep-wake cycle, and adversely affect our sleep. The colour of light we’re exposed to affects our biological clock time by changing levels of melatonin–the regulatory hormone of the circadian rhythm that initiates and maintains sleep. Short, blue wavelengths of bright daylight keep us awake by suppressing melatonin, while long, red wavelengths of a sunset allow melatonin secretion to signal our bodies to sleep. Like daylight, LED lamps emit light at blue wavelengths and effectively suppress melatonin and hinder sleep.
A study on the general US adult population found that living in areas with more lights is associated with later bedtimes, shorter sleep duration, and greater dissatisfaction with sleep quality. Ultimately, this leads to multiple problems such as: cognitive impairment, hindered moral decision making, and higher chance of injuries and accidents.
A bleak future?
Will we have to buy blackout curtains to protect our health when LED lamps take over? Hopefully not. Looking into improving sleep, the tactics of the city of Florida, Phoenix and towns in Connecticut may point us down the right path. These cities aimed to reduce LED health risks by lowering the amount of blue wavelengths emitted from street lamps. While differently coloured LEDs don’t affect brightness, they stray away from the wavelength that most negatively impacts our circadian rhythms. With cities using warmer-toned LED lamps, they solve the problem of energy- and cost-inefficient HPS lamps as well as blue LED lamps that compromise the health of citizens.

LEDs have different colour temperatures (K) ranging from warm yellow to cool blue. Bluer LEDs around 6000 K are commonly used in commercial and industrial applications like street lights. (Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Although a few cities are experimenting with sleep-friendly street lights, the majority are only looking to reduce costs. As cities push forward with their goals, it makes us question whether governments adequately consider citizens’ health.
(Credit: The Hindu)
Author: Olivia Wong